Can: How do miners make money on bitcoin
| Pvm money making rs3 |
| BITCOIN INVESTOR APP |
| How do miners make money on bitcoin |
| How do miners make money on bitcoin |
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
What Is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are entered into circulation. It is also the way the network confirms new transactions and is a critical component of the blockchain ledger's maintenance and development. "Mining" is performed using sophisticated hardware that solves an extremely complex computational best companies to invest in stocks philippines problem. The first computer to find the solution to the problem receives the next block of bitcoins and the process begins again.
Cryptocurrency mining is painstaking, costly, and only sporadically rewarding. Nonetheless, mining has a magnetic appeal for many investors who are interested in cryptocurrency because of the fact that miners receive rewards for their work with crypto tokens. This may be because entrepreneurial types see mining as pennies from heaven, like California gold prospectors in 1849. And if you are technologically inclined, why not do it?
The bitcoin reward that miners receive is an incentive that motivates people to assist in the primary purpose of mining: to legitimize and monitor Bitcoin transactions, ensuring their validity. Because many users all over the world share these responsibilities, how do miners make money on bitcoin, Bitcoin is a "decentralized" cryptocurrency, or one that does not rely on any central authority like a central bank or government to oversee its regulation.
However, before you invest the time and equipment, read this explainer to see whether mining is really for you.
Key Takeaways
- By mining, you can earn cryptocurrency without having to put down money for it.
- Bitcoin miners receive bitcoin as a reward for completing "blocks" of verified transactions, which are added to the blockchain.
- Mining rewards are paid to the miner who discovers a solution to a complex hashing puzzle first, and the probability that a participant will be the one to discover the solution is related to the portion of the network's total mining power.
- You need either a graphics processing unit (GPU) or an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) in order to set up a mining rig.
Click Play to Learn How Bitcoin Mining Works
Throughout, we use "Bitcoin" with a capital "B" when referring to the network or the cryptocurrency as a concept, and "bitcoin" with a small "b" when we're referring to a quantity of individual tokens.
Why Bitcoin Needs Miners
Blockchain "mining" is a metaphor for the computational work that nodes in the network undertake in hopes of earning new tokens. In reality, how do miners make money on bitcoin, miners are essentially getting paid for their work as auditors. They are doing the work of verifying the legitimacy of Bitcoin transactions. This convention is meant to keep Bitcoin users honest and was conceived by Bitcoin's founder, how do miners make money on bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto. By verifying transactions, miners are helping to prevent the "double-spending problem."
Double spending is a scenario in which a Bitcoin owner illicitly spends the same bitcoin twice. With physical currency, this isn't an issue: When you hand someone a $20 bill to buy a bottle of vodka, you no longer have it, so there's no danger you could use that same $20 bill to buy lotto tickets next door, how do miners make money on bitcoin. Though counterfeit cash is possible, it is not exactly the same as literally spending the same dollar twice. With digital currency, however, as the Investopedia dictionary explains, "there is a risk that the holder could make a copy of the digital token and send it to a merchant or another party while retaining the original."
Let's say you had one legitimate $20 bill and one counterfeit of that same $20. If you were to try to spend both the real bill and the fake one, someone who took the trouble of looking at both of the bills' serial numbers would see that they were the same number, and thus one of them had to be false. What a blockchain miner does is analogous to that—they check transactions to make sure that users have not illegitimately tried to spend the same bitcoin twice. This isn't a perfect analogy—we'll explain in more detail below.
Only 1 megabyte of transaction data can fit into a single bitcoin block. The 1MB limit was set by Satoshi Nakamoto, and this has become a matter of controversy because some miners believe the block size should increase to accommodate more data, which would effectively mean that the Bitcoin network could how do miners make money on bitcoin and verify transactions more quickly.
Why Mine Bitcoin?
In addition to lining the pockets of miners and supporting the Bitcoin ecosystem, mining serves another vital purpose: It is the only way to release new cryptocurrency into circulation. In other words, miners are basically "minting" currency. For example, as of March 2022, there were just under 19 million bitcoins in circulation, out of a total of 21 million.
Aside from the coins minted via the genesis block (the very first block, which founder Satoshi Nakamoto created), every single one of those bitcoins came into being because of miners. In the absence of miners, Bitcoin as a network would still exist and be usable, but there would never be any additional bitcoin. However, because the rate of bitcoin "mined" is reduced over time, the final bitcoin won't be circulated until around the year 2140. This does not mean that transactions will cease to be verified. Miners will continue to verify transactions and will be paid fees for doing so in order to keep the integrity of Bitcoin's network.
To earn new bitcoins, you need to be the first miner to arrive at the right answer, or closest answer, to a numeric problem. This process is also known as proof of work (PoW). To begin mining is to start engaging in this proof-of-work activity to find the answer to the puzzle.
No advanced math or computation is really involved. You may have heard that miners are solving difficult mathematical problems—that's true but not because the math itself is hard. What they're actually doing is trying to be the first miner to come up with a 64-digit hexadecimal number (a "hash") that is less than or equal to the target hash. It's basically guesswork.
So it is a matter of randomness, but with the total number of possible guesses for each of these problems numbering in the trillions, it's incredibly arduous work. And the number of possible solutions (referred to as the level of mining difficulty) only increases with each miner that joins the mining network. In order to solve a problem first, miners need a lot of computing power. To mine successfully, you need to have a high "hash rate," which is measured in terms gigahashes per second (GH/s) and terahashes per second (TH/s).
Aside from the short-term payoff of newly minted bitcoins, being a coin miner can also give you "voting" power when changes are proposed in the Bitcoin network protocol. This is known as a Bitcoin Improvement Protocol (BIP). In other words, miners have some degree of influence on the decision-making process for matters how do miners make money on bitcoin as forking. The more hash power you possess, the more votes you have to cast for such initiatives.
How Much a Miner Earns
The rewards for Bitcoin mining are reduced by half roughly every four years. When bitcoin was first mined in 2009, mining one block would earn you 50 BTC. In 2012, this was halved to 25 BTC. By 2016, this was halved again to 12.5 BTC. On May 11, 2020, the reward halved again to 6.25 BTC.
As of March 2022, the price of Bitcoin was around $39,000 per bitcoin, which means you'd have earned $243,750 (6.25 x 39,000) for completing a block. Not a bad incentive to solve that complex hash problem detailed above, it might seem.
To keep track of precisely when these halvings will occur, you can consult the Bitcoin Clock, which updates this information in real time. Interestingly, the market price of Bitcoin has, throughout its history, tended to correspond closely to the reduction of new coins entered into circulation. This lowering inflation rate increased scarcity and, historically, the price has risen with it.
If you want to estimate how much bitcoin you could mine with your mining rig's hash rate, the site CryptoCompare offers a helpful calculator. Other web resources offer similar tools.
What You Need to Mine Bitcoins
Although rsitez money making were able to compete for blocks with a regular at-home personal computer early on in Bitcoin's history, this is no longer the case. The reason for this is that the difficulty of mining Bitcoin changes over time.
In order to ensure the blockchain functions smoothly and can process and verify transactions, the Bitcoin network aims to have one block produced every 10 minutes or so. However, if there are 1 million mining rigs competing to solve the hash problem, they'll likely reach a solution faster than a scenario in which 10 mining rigs are working on the same problem. For that reason, Bitcoin is designed to evaluate and adjust the difficulty of mining every 2,016 blocks, or roughly every two weeks.
When there is more computing power collectively working to mine for bitcoins, the difficulty level of mining increases in order to keep block production at a stable rate, how do miners make money on bitcoin. Less computing power means the difficulty level decreases. At today's network size, a personal computer mining how do miners make money on bitcoin bitcoin will almost certainly find nothing.
Mining hardware
All of this is to say that, how do miners make money on bitcoin, in order to mine competitively, how do miners make money on bitcoin, miners must now invest in powerful computer equipment like a graphics processing unit (GPU) or, how do miners make money on bitcoin, more realistically, how do miners make money on bitcoin application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). These can run from $500 into the tens of thousands of dollars. Some miners—particularly Ethereum miners—buy individual graphics cards as a low-cost way to cobble together mining operations.
Today, Bitcoin mining hardware is almost entirely made up of ASIC machines, which in this case, specifically do one thing and one thing only: Mine for bitcoins. Today's ASICs are many orders of magnitude more powerful than CPUs or GPUs and gain both more hashing power and energy efficiency every few months as new chips are developed and deployed. Today's miners can produce almost 200 TH/s at only 27.5 joules per terahash.
An analogy
Say I tell three friends that I'm thinking of a number between one and 100, and I write that number on a piece of paper and seal it in an envelope. My friends don't have to guess the exact number; they just have to be the first person to guess any number that is less than or equal to it. And there is no limit to how many guesses they get.
Let's say I'm thinking of the number 19. If Friend A guesses 21, they lose because 21 > 19. If Friend B guesses 16 and Friend C guesses 12, then they've both theoretically arrived at viable answers because of 16 < 19 and 12 < 19. There is no "extra credit" for Friend B, even though B's answer was closer to the target answer of 19. How do miners make money on bitcoin imagine that I pose the "guess what number I'm thinking of" question, but I'm not asking just three friends, how do miners make money on bitcoin, and I'm not thinking of a number between 1 and 100. Rather, I'm asking millions of would-be miners, and I'm how do miners make money on bitcoin of a 64-digit hexadecimal number. Now you see that it's going to be extremely hard to guess the right answer. If B and C both answer simultaneously, then the system breaks down.
In Bitcoin terms, simultaneous answers occur frequently, but at the end of the day, there can only be one winning answer. When multiple simultaneous answers are presented that are equal to or less than the target number, the Bitcoin network will decide by a simple majority—51%—which miner to honor.
Typically, it is the miner who has done the most work or, in other words, the one that verifies the most transactions. The losing block then becomes an "orphan block." Orphan blocks are those that are not added to the blockchain. Miners who successfully solve the hash problem but haven't verified the most transactions are not rewarded with bitcoin.
The Mining Process
What Is a '64-Digit Hexadecimal Number'?
Here is an example of such a number:
0000000000000000057fcc708cf0130d95e27c5819203e9f967ac56e4df598ee
The number above has 64 digits. Easy enough to understand so far. As you probably noticed, that number consists not just of numbers, but also letters of the alphabet. Why is that?
To understand what these letters are doing in the middle of numbers, let's unpack the word "hexadecimal."
The decimal system uses factors of 100 as its base (e.g., 1% = 0.01). This, in turn, means that every digit of a multi-digit number has 100 possibilities, zero through 99. In computing, the decimal system is simplified to base 10, or zero through nine.
"Hexadecimal," on the other hand, means base 16 because "hex" is derived from the Greek word for six, and "deca" is derived from the Greek word for 10. In a hexadecimal system, each digit has 16 possibilities. But our numeric system only offers 10 ways of representing numbers (zero through nine). That's why you have to add letters, specifically, letters A, how do miners make money on bitcoin, B, C, D, E, how do miners make money on bitcoin F.
If you are mining Bitcoin, you do not need to calculate the total value of that 64-digit number (the hash). I repeat: You do not need to calculate the total value of a hash.
What do '64-digit hexadecimal numbers' have to do with Bitcoin mining?
Remember that analogy, in which the number 19 was written on a piece of paper and put in a sealed envelope? In Bitcoin mining terms, that metaphorical undisclosed number in the envelope is called the target hash.
What miners are doing with those huge computers and dozens of cooling fans is guessing at the target hash. Miners make these guesses by randomly generating as many "nonces" as possible, as quickly as possible. A nonce is short for "number only used once," and the nonce is the key to generating these 64-bit hexadecimal numbers I keep mentioning. In Bitcoin mining, a nonce is 32 bits in size—much smaller than the hash, which is 256 bits. The first miner whose nonce generates a hash that is less than or equal to the how do miners make money on bitcoin hash is awarded credit for completing that block and is awarded the spoils of 6.25 BTC.
In theory, you could achieve the same goal by rolling a 16-sided die 64 times to arrive at random numbers, but why on Earth would you want to do that?
The screenshot below, taken from the site Blockchain.info, might help you put all this information together at a glance. You are looking at a summary of everything that happened when block No.490163 was mined. The nonce that generated the "winning" hash was 731511405. The target hash is shown on top. The term "Relayed by AntPool" refers to the fact that this particular block was completed by AntPool, one of the more successful mining pools (more about mining pools below).
As you see here, their contribution to the Bitcoin community is that they confirmed 1,768 transactions for this block. If you really want to see all 1,768 of those transactions for this block, go to this page and scroll down to the Transactions section, how do miners make money on bitcoin.
Source: Blockchain.info
How do I guess at the target hash?
All target hashes begin with a string of leading zeroes. There is no minimum target, but there is a maximum target set by the Bitcoin Protocol. No target can be greater than this number:
00000000ffff0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
The winning hash for a bitcoin miner is one that has at least the minimum number of leading zeroes defined by the mining difficulty.
Here are some examples of randomized hashes and the tik tok app geld verdienen for whether they will lead to success tik tok app geld verdienen how do miners make money on bitcoin miner:
To find such a hash value, you have to get a fast mining rig, how do miners make money on bitcoin, or, more realistically, join a mining pool—a group of coin miners who combine their computing power and split the mined Bitcoin. Mining pools are comparable to Powerball clubs whose members buy lottery tickets en masse and agree to share any winnings. A disproportionately large number of blocks are mined by pools rather than by individual miners.
In other words, it's literally just a numbers game. You cannot guess the pattern or make a prediction based on previous target hashes. At today's difficulty levels, the odds of finding the winning value for a single hash is one in the tens of trillions. Not great odds if you're working on your own, even with a tremendously powerful mining rig.
Not only do miners have to factor in the costs associated with expensive equipment necessary to stand a chance of solving a hash problem, but they must also consider the significant amount of electrical power mining rigs utilize in generating vast quantities of nonces in search of the solution. All told, Bitcoin mining is largely unprofitable for most individual miners as of this writing. The site CryptoCompare offers a helpful calculator that allows you to plug in numbers such as your hash speed and electricity costs to estimate the costs and benefits.
Source: CryptoCompare
What Are Mining Pools?
The miner who discovers a solution to the puzzle first receives the mining rewards, and the probability that a participant will how do miners make money on bitcoin the one to discover the solution is equal to the proportion of the total mining power on the network.
Participants with a small percentage of the mining power stand a very small chance of discovering the next block on their own. For instance, a mining card that one could purchase for a couple of thousand dollars would represent less than 0.001% of the network's mining power. With such a how do miners make money on bitcoin chance at finding the next block, it could be a long time before that miner finds a block, and the difficulty going up makes things even worse. The miner may never recoup how do miners make money on bitcoin investment. The answer to this problem is mining pools.
Mining pools are operated by third parties and coordinate groups of miners. By working together in a pool and sharing the payouts among all participants, miners can get a steady flow of bitcoin starting the day they activate their miners. Statistics on some of the mining pools can be seen on Blockchain.info.
A Pickaxe Strategy for Bitcoin Mining
As mentioned above, the easiest way to acquire Bitcoin is to simply buy it on one of the many Bitcoin exchanges. Alternately, you can always leverage the "pickaxe strategy." This is based on the old saw that during the 1849 California Gold Rush, the smart investment was not to pan for gold, but rather to make the pickaxes used for mining.
To put it in modern terms, invest in the companies that manufacture those pickaxes. In a cryptocurrency context, the pickaxe equivalent would be a company that manufactures equipment used for Bitcoin mining. You may consider looking into companies that make ASIC equipment or GPUs instead, for example.
Downsides of Mining
The risks of mining are often financial and regulatory. As aforementioned, Bitcoin mining, and mining in general, is a financial risk because one could go through all the effort of purchasing hundreds or thousands of dollars worth of mining equipment only to have no return on their investment. That said, this risk can be mitigated by joining mining pools. If you are considering mining and real money making surveys in an area where it is prohibited, you should reconsider. It may also be a good idea to research your country's regulation and overall sentiment toward cryptocurrency before investing in mining equipment.
One additional potential risk from the growth of Bitcoin mining (and other PoW systems as well) is the increasing energy usage required by the computer systems running the mining algorithms. Though microchip efficiency has increased dramatically for ASIC chips, the growth of the network itself is outpacing technological progress. As a result, there are concerns about Bitcoin mining's environmental impact and carbon footprint.
There are, however, efforts to mitigate this negative externality by seeking cleaner and green energy sources for mining operations (such as geothermal or solar sources), as well as utilizing carbon offset credits. Switching to less energy-intensive consensus mechanisms like proof-of-stake (PoS), which Ethereum has transitioned to, is another strategy; however, PoS comes with its own set of drawbacks and inefficiencies, such as incentivizing hoarding instead of using coins and a risk of centralization of consensus control.
Mining is a metaphor for introducing new bitcoins into the system because it requires (computational) work just as mining for gold or silver requires (physical) effort. Of course, the tokens that miners find are virtual and exist only within the digital ledger of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Why Do Bitcoins Need to Be Mined?
Because they are entirely digital records, there is a risk of copying, counterfeiting, or double-spending the same coin more than once. Mining solves these problems by making it extremely expensive and resource-intensive to try to do one of these things or otherwise "hack" the network. Indeed, it is far more cost-effective to join the network as a miner than to try to undermine it.
How Does Mining Confirm Transactions?
In addition to introducing new BTC into circulation, mining serves the crucial role of confirming and validating new transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. This is important because there is no central authority such as a bank, court, government, or anything else determining which transactions are valid and which are not. Instead, the mining process achieves a decentralized consensus through proof of work (PoW).
Why Does Mining Use So Much Electricity?
In the early days of Bitcoin, anybody could simply run a mining program from their PC or laptop. But as the network got larger and more people became interested in mining, the mining algorithm became more difficult. This is because the code for Bitcoin targets finding a new block once every 10 minutes, on average. If more miners are involved, the chances that somebody will solve the right hash quicker increases, and so the difficulty increases to restore that 10-minute goal. Now imagine if thousands, or even millions more times that mining power joins the network. That's a lot of new machines consuming energy.
Is Bitcoin Mining Legal?
The legality of Bitcoin mining depends entirely on your geographic location. The concept of Bitcoin can threaten the dominance of fiat currencies and government control over the financial markets. For this reason, Bitcoin is completely illegal in certain places.
Bitcoin ownership and mining are legal in more countries than not. Some examples of places where it was illegal according to a 2018 report were Algeria, Egypt, Morocco, Bolivia, Ecuador, Nepal, and Pakistan. Since 2018, other countries have banned Bitcoin mining how do miners make money on bitcoin Bangladesh, China, Dominican Republic, North Macedonia, Qatar, how do miners make money on bitcoin, and Vietnam. Overall, How do miners make money on bitcoin use and mining remain legal across much of the globe.
Does Crypto Mining Damage Your GPU/Computer?
Because blockchain mining is very resource-intensive, it can put a large strain on your GPU or other mining hardware. In fact, it is not unheard of for GPUs to blow out, or for mining rigs to burst into flames. However, how do miners make money on bitcoin, keeping your rigs running at a moderate pace and with sufficient power supplied, it is generally safe.
Can You Mine Bitcoin on Your iPhone?
No. Bitcoin mining today requires vast amounts of computing power and electricity to be competitive. Running a miner on a mobile device, even if it is part of a mining pool, will likely result in no earnings.
The Bottom Line
Bitcoin "mining" serves a crucial function to validate and confirm new transactions to the blockchain and to prevent double-spending by bad actors. It is also the way that new bitcoins are introduced into the system. Based on a complex puzzle, the task involves producing proof of work (PoW), how do miners make money on bitcoin, which is inherently energy-intensive. This energy, however, is embodied in the value of bitcoins and the Bitcoin system and keeps this decentralized system stable, how do miners make money on bitcoin, secure, and trustworthy.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Bitcoin mining is designed to be similar to gold mining in many ways. This “digital mining” is a computer process that creates new Bitcoin, in addition to tracking Bitcoin transactions and ownership. Bitcoin mining and gold mining are both energy intensive, and both have the potential to generate a handsome monetary reward.
Let’s dig further in Bitcoin mining to learn about how it works and how it influences Bitcoin transactions and Bitcoin investors.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin mining is a process of verifying and recording new Bitcoin transactions.
- Bitcoin miners are paid with transaction fees and newly created digital currency.
- Many Bitcoin miners use specialized mining hardware and participate in mining pools.
- Cryptocurrency mining can be highly energy intensive, requiring access to a low-cost energy source to be profitable.
What Is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is a highly complex computing process that uses complicated computer code to create a secure cryptographic system. Similar to the secret codes used by governments and spies, the cryptography used for real money making surveys generates Bitcoin, facilitates Bitcoin transactions, and tracks asset ownership of the cryptocurrency. Bitcoin mining supports the Bitcoin database, which is called the blockchain.
Bitcoin miners are not people with picks and shovels, how do miners make money on bitcoin rather owners of sophisticated computing equipment. Bitcoin miners compete to be the first to verify Bitcoin transactions, and earn rewards paid in Bitcoin. Crypto miners need to first invest in computer equipment that is specialized for mining, and typically require access to a low-cost energy source.
While anyone can mine Bitcoin, because of the required computing power and energy usage, it’s tough to profit from Bitcoin mining.
The competing miners race to complete challenging mathematical functions, called hashes, to process Bitcoin transactions. A miner’s hashrate is the speed at which their configuration of computers is able to solve the mathematical equations. This mining protocol is called proof of work, because the first miner to prove that they have done the “work” of solving a complex equation earns the right to process the newest block of Bitcoin transactions.
After a miner successfully verifies a new block of transactions, the block is distributed to all other miners and any other device with a full copy investment in share market tips the Bitcoin blockchain. (These devices are called nodes.) Many computers worldwide keep identical copies of the blockchain, ensuring the creation and maintenance of a trusted, verified history that’s nearly impossible to hack or distort.
Why Mine Bitcoin?
There are two main reasons to mine Bitcoin. One is to earn a profit from Bitcoin mining, which is possible under the right circumstances. The second is to learn more about how cryptocurrencies work and support the ongoing peter leeds invest in penny stocks of the Bitcoin network. Let’s take a look at each of these reasons to mine Bitcoin:
Bitcoin Mining for Profit
If you’re interested in mining Bitcoin on your own, known as solo mining, and want to earn a profit, then you likely need specialized mining hardware. How do miners make money on bitcoin with a graphics processing unit (GPU) or application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is generally the most effective, although computers like your laptop or desktop (which rely on a central processing unit chip to handle its basic functions) can also be used.
In addition to expensive hardware, you’ll have to consider internet bandwidth availability and your local power costs. Bitcoin mining uses a large amount of electricity. To profit, how do miners make money on bitcoin, you need access to low-cost power or perhaps solar panels on your roof. You also need an internet service provider that allows unlimited internet usage without charging fees for going over a specific data limit.
Some Bitcoin miners join forces with other miners to form Bitcoin mining how do miners make money on bitcoin. Groups of miners working together have better chances of earning rewards, and share their profits among themselves. Members of a mining pool pay a fee for the mining pool membership.
Bitcoin Mining for Fun and Education
If you enjoy tinkering with computers and learning about emerging technologies, then you may want to mine Bitcoin even if you don’t make money. Setting up your own Bitcoin mining configuration can teach you about the inner workings of your computer as well as the Bitcoin network.
How To Start Mining Bitcoin
Curious about exactly how to mine Bitcoin? Bitcoin mining how do miners make money on bitcoin simple, but anyone with intermediate to advanced computer skills is probably qualified. If you’ve reviewed the potential want to get started with Bitcoin mining, then follow these basic steps:
Choose Your Bitcoin Mining Hardware
Your first step is choosing the hardware you’ll how to calculate return on stock investment in excel to mine Bitcoin. Many people start with an old computer to get a basic idea of how Bitcoin mining works. If you want to earn a profit, it’s important to use optimized mining hardware, such as a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) or Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) miner.
Other minimum requirements for Bitcoin mining include a high-speed internet connection of at least 50 kilobytes per second, how do miners make money on bitcoin, plus no restrictions on data uploads and downloads. Bitcoin mining nodes commonly use up to 200 gigabytes of data per month for uploads, and around 20 gigabytes per month for data downloads.
Decide Between Solo and Pooled Mining
Next, you can decide between mining on your own and teaming up with other miners. Because solo mining is less likely to be consistently profitable, many individuals join a mining pool for more predictable crypto rewards.
Install and Configure Bitcoin Mining Software
Now it’s time to install your Bitcoin mining software. Depending on your hardware, operating system, and other factors, you can choose among different mining applications. Here’s a look at some of the how do miners make money on bitcoin popular cryptocurrency mining software.
You also need to link your mining setup to a Bitcoin wallet, preferably a dedicated one for Bitcoin. Miners use crypto wallets to collect rewards.
Begin Mining for Bitcoin
Once your mining rig is fully configured, you can click the button to start mining. Then sit back and watch your computer hustle to earn Bitcoin. Mining rigs typically need to run at least six hours each day to be functionally successful, though letting your mining rig run all the time increases the likelihood of earning rewards from Bitcoin mining.
Monitor and Fine Tune Your Mining Rig
Bitcoin mining is passive, but it’s not entirely set-it-and-forget-it. You’ll want to monitor your mining rig’s performance and energy use to ensure that your mining operation is running as efficiently and profitably as possible. Sometimes a small configuration change can significantly improve your earnings.
Risks and Limitations of Bitcoin Mining
If you do decide to mine for Bitcoin, consider these risks and limitations:
Electricity Use
The Bitcoin network, which includes miners, nodes, and Bitcoin users, consumes more energy than many countries. As of January 16, 2022, the Bitcoin network consumes 131.00 TWh (that’s terawatt-hours) of electricity annually, meaning that Bitcoin uses more electricity than countries such as Norway and the Ukraine, and a little less than Egypt and Poland.
Mining for the largest cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin requires the most invest google stock because competition to earn Bitcoin rewards is the fiercest.
Bandwidth Use
Bitcoin miners constantly download and upload data. It’s best to only mine for Bitcoin bitcoin investors forum 18 an unmetered, unlimited internet connection, how do miners make money on bitcoin. If you have to pay for every megabyte or gigabyte used or encounter data caps, similar to most cell phone plans, then you could use more data than is allowed—and have your internet connection cut or face additional charges. In general, most Bitcoin miners don’t use all that much data on an ongoing basis.
Hardware Damage
Bitcoin mining how do miners make money on bitcoin a highly intense process for computer hardware units. If your mining system is set up correctly, you shouldn’t need to worry about hardware damage beyond normal wear and tear. But choosing the wrong hardware or running a mining configuration with poor ventilation can overheat and damage your machine.
Bitcoin Supply and Reward Constraints
Bitcoin mining becomes by design periodically more difficult. Every year, the number of Bitcoins created per block is halved. Once 21 million bitcoin have been minted, no new bitcoins will be created. From that point onward, Bitcoin miners will profit solely from transaction fees.
The reward for mining Bitcoin decreases as the amount of unmined Bitcoin declines. “Halving,” or a 50% reduction in rewards for Bitcoin miners, occurs every time another 210,000 blocks of Bitcoin are mined. Bitcoin mining rewards are halved approximately every four years.
In 2009, when Bitcoin was launched, the reward for successfully mining a Bitcoin block was 50 bitcoins. The first halving occurred in 2012, reducing the mining reward to 25 bitcoins. Halving has occurred twice since 2012, with the last instance in May, 2020, how do miners make money on bitcoin. The current reward for mining a block of Bitcoin is 6.25 BTC, and the next halving is expected in 2024.
Taxes
As with any other income-generating activity, profits from Bitcoin mining are taxable. It’s essential to track cryptocurrency transactions for tax purposes, since how do miners make money on bitcoin tax liabilities could get you in trouble with Uncle Sam.
Geographical Limitations
Bitcoin and Bitcoin mining are not how do miners make money on bitcoin everywhere. China, for example, outlawed all cryptocurrency activities in 2021. Be sure to understand the rules and regulations, pertaining to Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, in the region where you reside or are considering establishing a mining operation.
The Bottom Line on Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is essential to the functionality of Bitcoin. Miners do the vital work of verifying transactions, tracking Bitcoin asset ownership, and ensuring the Bitcoin network remains secure. Almost anyone can participate using a computer capable of Bitcoin mining. Even if you don’t plan on mining, it’s good for Bitcoin users to understand the basics behind how Bitcoin mining works.
Frequently How to make lego candy machine that takes money Questions (FAQs)
How much money can you make mining Bitcoin?
Bitcoin miners earn rewards, paid in Bitcoin, for verifying a new block of Bitcoin transactions. Miners who successfully validate a block earn a reward of 6.25 bitcoins–currently worth more than $260,000. Many miners work together in mining pools, enabling them to earn typically lower rewards but more frequently.
How do you join a Bitcoin mining pool?
If you have hardware that meets the pool’s requirements, then you can download that pool’s specific software or other compatible mining software. You can connect your mining client to the mining pool using a network address and other configurations that your mining pool operator provides.
What is a good hashrate for Bitcoin mining?
A mining computer’s total hashrate, or calculations per second, denotes the mathematical processing power of a computer or group of computers mining Bitcoin. Higher hashrates rates are better. As mining difficulty increases, your mining rig needs a higher hashrate to compete with other miners. High-end mining hardware for Bitcoin has a hashrate of around 100 hashes per second.
How much bandwidth does Bitcoin mining use?
To mine for Bitcoin, you’ll want to use a high-speed broadband internet connection. How do miners make money on bitcoin your rig is up and running, total data uploads and downloads are typically minimal because your mining rig can solve complex math equations without using much data. You need a connection with minimum upload speeds of at least 50 kilobytes per second for successful Bitcoin mining.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
When Bitcoin (CRYPTO:BTC) was launched in 2009, it introduced the concept of Bitcoin mining. Miners are responsible for confirming transactions and for the creation of new coins; they receive Bitcoin rewards for their efforts.
Considering Bitcoin's value, getting it as a reward is an enticing proposition. No doubt most of us have at least briefly considered Bitcoin mining after first hearing about it. When you dig a little deeper, however, you find it's not nearly as great as it sounds. In this guide, we'll cover exactly how it works and whether Bitcoin mining is worth it in 2022.

Image source: Getty Images.
What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process how do miners make money on bitcoin validating Bitcoin transactions and minting new coins. Since Bitcoin is decentralized, there's no central authority managing transactions or issuing coins like there is with government-backed currencies. Bitcoin miners, who can be anyone, handle this instead.
To record transactions, Bitcoin uses a blockchain, a public ledger that contains all of Bitcoin's transactions. Miners check each block, and, once they confirm it, they add it to the blockchain.
For helping to keep the network secure, miners earn Bitcoin rewards as they add blocks. The rewards are paid using transaction fees and through the creation of new Bitcoin. However, there is a fixed maximum supply of 21 million Bitcoins. Once that many are in circulation, rewards will be paid entirely using transaction fees.
How Bitcoin mining works
The Bitcoin mining process always starts with a block that contains a group of transactions. The transactions have already gone through an initial security check by the network to verify that the sender has enough Bitcoin and has provided the correct key to their wallet.
Here's what occurs next to how do miners make money on bitcoin a block:
- The network creates a hash (a string of characters) for the block of transactions. Bitcoin uses an algorithm called SHA-256 to do this, and it always generates hashes with 64 characters.
- Bitcoin miners start generating hashes using mining software. The goal is to generate the target hash-- one that's below or equal to the block's hash.
- The first miner to generate the target hash gets to attach the block to their copy of the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Other miners and Bitcoin security nodes check that the block is correct. If so, the block is added to the official Bitcoin blockchain.
- The Bitcoin miner then receives block rewards. Blocks offer a set amount of Bitcoin as a reward; the amount is cut in half for every 210,000 blocks that are mined (this is called Bitcoin halving).
This system Bitcoin uses is called proof of work because miners need to prove they expended computing power during the mining process. They do this when they provide the target hash.
One important thing to know about Bitcoin mining is that the network varies the difficulty to maintain an output of one block every 10 minutes. When more miners join, or they start using mining devices with more processing power, mining difficulty increases.
Types of cryptocurrency mining
There are several types of cryptocurrency mining depending on the method you choose. Here are the most popular ways to mine Bitcoin.
ASIC mining
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is a specialized device built for one purpose, and ASIC miners are designed for mining a specific cryptocurrency. These are the most powerful option for Bitcoin mining. New ASICs can cost thousands of dollars, but they're also the only type of device where you can potentially make a profit from Bitcoin mining.
GPU mining
GPU mining uses one or more graphics cards to mine crypto, how do miners make money on bitcoin. A typical "mining rig" is a computer that has one or more high-end graphics cards, how do miners make money on bitcoin. This kind of mining is costly up front because you need to buy the graphics cards, how do miners make money on bitcoin. Although it's popular for mining other types of cryptocurrency, it doesn't work well for Bitcoin due to the lack of power compared to ASICs.
CPU mining
CPU mining uses a computer's central processing unit, how do miners make money on bitcoin. This is the most accessible way to mine crypto since all you need is a computer, and it worked in the early days of Bitcoin. It's no longer recommended for mining Bitcoin because CPUs don't have nearly enough processing power to compete with ASICs.
Cloud mining
Cloud mining involves paying a company to mine crypto for you. Instead of setting up your how do miners make money on bitcoin mining device, you're essentially renting one and receiving the profits after maintenance and electricity costs are deducted. While it may sound like a good deal at a glance, how do miners make money on bitcoin, cloud mining normally requires committing to a contract, and, if crypto prices fall, you're unlikely to break even.
Mining pools
A mining pool is a group of crypto miners who pool their resources and share rewards. By working together, miners are much more likely to get the chance to mine new blocks. With Bitcoin mining, it's very difficult to mine blocks if you're operating solo. Each how do miners make money on bitcoin pool has its own hardware requirements, with most requiring you to have either an ASIC miner or a GPU.
Is Bitcoin mining profitable?
Bitcoin mining usually isn't profitable for individuals anymore because of the costs involved and the competition.
Here are the main factors that determine how much you can make mining Bitcoin:
- Cost of the mining device: Quality ASICs range from about $1,000 to more than $15,000.
- Hash rate: The hashes per second the mining device can generate. The higher this is, the more you earn. This is expressed as terahashes per second (TH/s), or how many trillions of hashes the device generates per second.
- Efficiency: The amount of energy a mining device requires. This is expressed as watts per terahash (W/TH), or the number of watts the device needs to generate a trillion hashes.
- Electricity costs: The price you pay is it worth investing in stocks and shares isa now electricity. The only way to make money mining Bitcoin is with cheap electricity.
- Price of Bitcoin: Bitcoin is extremely volatile, and the amount you earn will rise or fall with its price movements.
Fortunately, you don't need to do the math yourself. There are plenty of mining profitability calculators available. Plug in how much you pay for electricity, and the calculator will tell you how much passive income you can expect to earn per day, how do miners make money on bitcoin, per month, and per year.
Divide the earnings by the cost of the mining device to find out how long it will take before you're turning a profit. In most cases, it's more than a year and often more than two. Keep in mind that it could end up taking even longer because how do miners make money on bitcoin mining difficulty increases.
The other problem is that mining devices have a limited lifespan. With proper maintenance and care, three to five years is about average, but they're often obsolete by the three-year mark.
To sum it up, Bitcoin mining offers very how do miners make money on bitcoin profitability at best and requires a big initial financial commitment. It makes more sense to learn how to invest in cryptocurrency and put that money into buying coins.
How to start Bitcoin mining
Here's a quick guide for how to start Bitcoin mining:
- Buy an ASIC miner. You can find them at many online retailers, how do miners make money on bitcoin, including Amazon (NASDAQ:AMZN), eBay (NASDAQ:EBAY), and Newegg (NASDAQ:NEGG).
- Choose a location to set up your ASIC. Miners generate quite a bit of heat, so it needs to be an area with good air circulation, how do miners make money on bitcoin. You'll bitcoin investeren 0 5 need a 220V outlet.
- Set up a crypto wallet to safely store cryptocurrency. There are free crypto wallets you can download, as well as hardware wallets that offer more security and generally cost $50 to $150.
- Join a mining pool. Because of how difficult mining Bitcoin is now, being part of a mining pool is a must.
As previously noted, there are different ways to mine Bitcoin, and the process is different depending on which one you choose. The best way to how do miners make money on bitcoin a reasonable chance at making a profit is with an ASIC and a mining pool.
Understanding the risks of Bitcoin mining
The biggest risk of Bitcoin mining is that you won't make back your start-up costs. ASIC miners aren't cheap, and those with sufficient processing power normally cost at least $1,000. Although you can find cheaper options, remember that paying less also means earning less.
It's possible to make your money back and eventually profit, but mining earnings are far from stable. If the price of Bitcoin drops, so do your earnings. And an increase in mining difficulty can cut into any profits.
While prospective miners often focus on profitability, there's also the safety aspect to consider. Bitcoin mining uses a substantial amount of electricity. It's notoriously bad for the environment, and it can be a safety hazard if you're not careful.
Mining devices can damage your home's electrical system or overload the power grid. There have also been reports of fires in poorly designed mining farms without proper cooling.
Is Bitcoin mining worth it?
If you run the numbers, you're most likely going to find that Bitcoin mining isn't worth it for you. It typically takes at least a year, and potentially more than two years, before you break even on the cost of your mining rig. That's assuming you don't run into any issues such as problems with your electrical grid or the price of Bitcoin plummeting.
You're better off buying Bitcoin with the money you planned to invest in mining. If the price increases, you'll be up on your investment, which wouldn't be the case if you were still waiting to recoup the cost of a miner. You could also consider different types of crypto investments. Here are a few options available on the stock market:
Alternatively, you can invest in cryptocurrencies directly by buying them on cryptocurrency exchanges. Money making electronic projects are plenty of investment options available, so it's simply a matter of choosing the one that fits you best.
What Is Bitcoin? BTC Price and How It Works
BTC definition: What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a form of digital cash that eliminates the need for central authorities such as banks or governments. Instead, Bitcoin uses a peer-to-peer internet network to confirm purchases directly between users.
Launched in 2009 by a mysterious developer known as Satoshi NakamotoBitcoin.org. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Accessed Mar 17, 2022.
View all sources
, Bitcoin (BTC) was the first, and most valuable, entrant in the emerging class of assets known as cryptocurrencies.Bitcoin price
The following chart shows current and historical Bitcoin price data.
How does Bitcoin work?
Each Bitcoin is a file stored in a digital wallet on a computer or smartphone. To understand how the cryptocurrency works, it helps to understand these terms and a little context:
Blockchain: Bitcoin is powered by open-source code known as blockchain, which creates a shared public history of transactions organized into "blocks" that are "chained" together to prevent tampering. This technology creates a permanent record of each transaction, how do miners make money on bitcoin, and it provides a way for every Bitcoin user to operate with the same understanding of who owns what.
Private and public keys: A Bitcoin wallet contains a public key and a private key, which work together to allow the owner to initiate and digitally sign transactions, how do miners make money on bitcoin. This unlocks the central function of Bitcoin — securely transferring ownership from one user to another.
Bitcoin mining: Users on the Bitcoin network verify transactions through a process known as mining, which is designed to confirm that new transactions are consistent with other transactions that have been completed in the past. This ensures that you can’t spend a Bitcoin you don’t have, or that you have previously spent.
» Ready to invest in Bitcoin? Our picks for the best Bitcoin and cryptocurrency exchanges.
Advertisement
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
NerdWallet ratingNerdWallet's ratings are determined by our editorial team. The scoring formula for online brokers and best way to invest money for retirement income takes into account over 15 factors, how do miners make money on bitcoin, including account fees and minimums, investment choices, customer support and mobile app capabilities. | NerdWallet ratingNerdWallet's ratings are determined by our editorial team. The scoring formula for online brokers and robo-advisors takes into account over 15 factors, including account fees and minimums, how do miners make money on bitcoin, investment choices, customer support and mobile app capabilities. | NerdWallet ratingNerdWallet's ratings are determined by our editorial team. The scoring formula for online brokers and robo-advisors takes into account over 15 factors, how do miners make money on bitcoin, including account fees and minimums, investment choices, customer support and mobile app capabilities. |
Learn More | Learn More | Learn More |
Fees0.5% - 4.5% varies by type of transaction; other fees may apply | Fees0.5% - 3.99% depending on payment method and platform | |
How does Bitcoin make money?
New Bitcoins are created as part of the Bitcoin mining process, in which they are offered as a lucrative reward to people who operate computer systems that help to validate transactions.
Bitcoin miners — also known as "nodes" — are the owners of high-speed computers which independently confirm each transaction, and add a completed "block" of transactions to the ever-growing how do miners make money on bitcoin which has a complete, public and permanent record of every Bitcoin transaction.
Miners are paid in Bitcoin for their efforts, which incentivizes the decentralized network to independently verify each transaction. This independent network of miners also decreases the chance for fraud or false information to be recorded, as the majority of miners need to confirm the authenticity of each block of data before it's added to the blockchain, how do miners make money on bitcoin, in a process known as "proof of work."
» Learn more: What is blockchain, and how does it work?
How do I start mining Bitcoin?
As Bitcoin has grown in popularity and value, competition for the rewards offered by mining has grown steeper. Most miners now use specialized computers designed just for that purpose. This equipment uses a huge amount of energy, a cost that can be another barrier to entry.
All of this means Bitcoin mining is a difficult proposition for a beginner, though some smaller operators choose to join mining pools in which they combine their computing power with others in an attempt to compete for rewards.
If you’re interested in getting started, a first step would be to research some popular mining pools and what they require.
Can Bitcoin be converted to cash?
Like many other assets, Bitcoin can be bought and sold with fiat currencies such as the U.S. dollar. The price will depend on the current market value, which can fluctuate significantly from day to day.
If you’re looking to buy or sell Bitcoin, you have a handful of choices. But for most beginners, the simplest approach is using a cryptocurrency exchange.
Some of these making money raising cattle operated by online stock brokerages, and others are independent. But given Bitcoin’s prominence in the market, you can trade it at pretty much any platform that offers crypto.
Here are some other options for buying and selling Bitcoin:
You decide: Is Bitcoin a good investment?
Bitcoin, and cryptocurrencies in general, are a volatile asset class. A common rule of thumb is to devote only a small portion of a diversified portfolio to risky investments such as Bitcoin or individual stocks.
Whether or not Bitcoin is a good investment for you depends on your individual circumstances, but here are a few pros and cons of Bitcoin to consider.
Bitcoin pros
Private, secure transactions anytime — with fewer potential fees. Once you own Bitcoin, you can transfer them anytime, how do miners make money on bitcoin, reducing the time and potential expense of any transaction. Transactions don’t contain personal information like a name or credit card number, which eliminates the risk of consumer information being stolen for fraudulent purchases or identity theft.
The potential for big growth. Some investors who buy and hold the currency are betting that once Bitcoin matures, greater trust and more widespread use will follow, and therefore Bitcoin’s value will grow.
Decentralization. After the financial crisis and the Great Recession, some investors are eager to embrace an alternative, decentralized currency — one that is essentially outside the control of regular banks, governing authorities or other third parties.
» Learn how to invest in Bitcoin
Bitcoin cons
Price volatility, how do miners make money on bitcoin. While Bitcoin's value has risen dramatically over the years, buyers' fortunes have varied widely depending on the timing of their investment. Those who bought in 2017 when Bitcoin’s price was racing toward $20,000, for example, had to wait until December 2020 to recover their losses. And even though 2021 was a strong period for Bitcoin, it has since fallen substantially off of its all-time highs.
Hacking concerns. While backers say the blockchain technology behind Bitcoin is even more secure than traditional electronic money transfers, there have been a number of high-profile hacks. In May 2019, for instance, more than $40 million in Bitcoin was stolen from several high-net-worth accounts on cryptocurrency exchange Binance. (The company covered the losses.)
Limited (but growing) use. A handful of merchants have begun accepting Bitcoin as payment. But these companies are the exception, not the rule.
Not protected by SIPC. The Securities Investor Protection Corporation insures investors up to $500,000 if a brokerage fails or funds are stolen, but that insurance doesn’t cover cryptocurrencyFINRA. Cryptocurrency How do miners make money on bitcoin Platforms: Do Your Homework. Accessed Mar 17, 2022.
View all sources
.
» Beyond Bitcoin: What are altcoins, and how do they work?
It pays to have a Nerdy expert
With a NerdWallet Plus subscription, get financial coaching, identity theft protection, and custom budgeting tools — all approved by the Nerdy experts.

Storing your Bitcoins: Hot wallets vs. cold wallets
If you decide to buy Bitcoin, you’ll need a place to store it. Bitcoins can be stored in two kinds of digital wallets:
Hot wallet: You can often store cryptocurrency on exchanges where it is sold. Other providers offer standalone online storage. Such solutions provide access through a computer browser, desktop or smartphone app.
Cold wallet: An encrypted portable device best money making runescape 2022 f2p like a thumb drive that allows you to download and carry your Bitcoins.
Basically, a hot wallet is connected to the internet; a cold wallet is not. But you need a hot wallet to download Bitcoins into a portable cold wallet.
» Learn more: What's the best Bitcoin wallet for you?
Disclosure: The author held no positions in how do miners make money on bitcoin aforementioned investments at the original time of publication.
Bitcoin
Decentralized digital currency
"₿" redirects here. Not to be confused with "฿" for Thai baht.
| Bitcoin | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Plural | bitcoins |
| Symbol | ₿ (Unicode: U+20BF ₿BITCOIN SIGN (HTML ₿))[a] |
| Code | BTC,[b] XBT[c] |
| Precision | 10−8 |
| Subunits | |
| 1⁄1000 | millibitcoin |
| 1⁄1000000 | microbitcoin |
| 1⁄100000000 | satoshi[2] |
| Original author(s) | Satoshi Nakamoto |
| White paper | "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System"[4] |
| Implementation(s) | Bitcoin Core |
| Initial release | 0.1.0 / 9 January 2009 (13 years ago) (2009-01-09) |
| Latest release | 22.0 / 13 September 2021 (6 months ago) (2021-09-13)[3] |
| Code repository | github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin |
| Development status | Active |
| Website | bitcoin.org |
| Ledger start | 3 January 2009 (13 years ago) (2009-01-03) |
| Timestamping scheme | Proof-of-work how do miners make money on bitcoin hash inversion) |
| Hash function | SHA-256 (two rounds) |
| Issuance schedule | Decentralized (block reward) Initially ₿50 per block, halved every 210,000 blocks[7] |
| Block reward | ₿6.25[d] |
| Block time | 10 minutes |
| Circulating supply | ₿18,925,000[e] |
| Supply limit | ₿21,000,000[5][f] |
| Exchange rate | Floating |
| Market cap | >US$775 billion[g] |
| Official user(s) | |
| |
Bitcoin (₿) is a decentralized digital currency, without a central bank or single administrator, that can be sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network without the need for intermediaries.[7] Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain. The cryptocurrency was invented in 2008 by an unknown person or group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto.[9] The currency began use in 2009[10] when its implementation was released as open-source software.[6]: ch. 1
Bitcoins are created as a reward for a process known as mining. They can be exchanged for other currencies, products, and services. Bitcoin has been criticized for its use in illegal transactions, the large amount of electricity (and thus carbon footprint) used by mining, price volatility, and thefts from exchanges. Some investors and economists have characterized it as a speculative bubble at various times. Others have used it as an investment, how do miners make money on bitcoin, although several regulatory agencies have issued investor alerts about bitcoin.[11][12][13]
A few local and national governments are officially using Bitcoin in some capacity, with one country, El Salvador, adopting it as a legal tender.
The word bitcoin was defined in a white paper published on 31 October 2008.[4][14] It is a compound of the words bit and coin.[15] No uniform convention for bitcoin capitalization exists; some sources use Bitcoin, capitalized, to refer to the technology and network and bitcoin, lowercase, for the unit of account.[16]The Wall Street Journal,[17]The Chronicle of Higher Education,[18] and the Oxford English Dictionary[15] advocate the use of lowercase bitcoin in all cases.
Design
Units and divisibility
The unit of account of the bitcoin system is the bitcoin. Currency codes for representing bitcoin are BTC[a] and XBT.[b][22]: 2 Its Unicode character is ₿.[1] One bitcoin is divisible to eight decimal places.[6]: ch. 5 Units for smaller amounts of bitcoin are the millibitcoin (mBTC), equal to 1⁄1000 bitcoin, and the satoshi (sat), which is the smallest possible division, and named in homage to bitcoin's creator, representing 1⁄100000000 (one hundred millionth) bitcoin.[2] 100,000 satoshis are one mBTC.[23]
Blockchain

The bitcoin blockchain is a public ledger that records bitcoin transactions.[26] It is implemented as a chain of blocks, each block containing a hash of the previous block up to the genesis block[c] in the chain, how do miners make money on bitcoin. A network of communicating nodes running bitcoin software maintains the blockchain.[27]: 215–219 Transactions of the form payer X sends Y bitcoins to payee Z are broadcast to this network using readily available software applications.
Network nodes can validate transactions, add them to their copy of the ledger, and then broadcast these ledger additions to other nodes. To achieve independent verification of the chain of ownership each network node stores its own copy of the blockchain.[28] At varying intervals of time averaging to every 10 minutes, how do miners make money on bitcoin, a new group of accepted transactions, called a block, is created, added to the blockchain, and quickly published to all nodes, without requiring central oversight. This allows bitcoin software to determine when a particular bitcoin was spent, which is needed to prevent double-spending. A conventional ledger records the transfers of actual bills or promissory notes that exist apart from it, but the blockchain is the only place that bitcoins can be said to exist in the form of unspent outputs of transactions.[6]: ch. 5
Individual blocks, public addresses and transactions within blocks can be examined using a blockchain explorer.[citation needed]
Transactions
See also: Bitcoin network
Transactions are defined using a Forth-like scripting language.[6]: ch. 5 Transactions consist of one or more inputs and one or more outputs. When a user sends bitcoins, the user designates each address and the amount of bitcoin being sent to that address in an output. To prevent double spending, each input must refer to a previous unspent output in the blockchain.[29] The use of multiple inputs corresponds to the use of multiple coins in a cash transaction. Since transactions can have multiple outputs, users can send bitcoins to multiple recipients in one transaction. As in a cash transaction, the sum of inputs (coins used to pay) can exceed the intended sum of payments. In such a case, an additional output is used, returning the change back to the payer.[29] Any input satoshis not accounted for in the transaction outputs become the transaction fee.[29]
Though transaction fees are optional, miners can choose which transactions to process and prioritize those that pay higher fees.[29] Miners may choose transactions based on the fee paid relative to their storage size, not the absolute amount of money paid as a fee. These fees are generally measured in satoshis per byte (sat/b). The size of transactions is dependent on the number of inputs used to create the transaction, and the number of outputs.[6]: ch. 8
The blocks in the blockchain were originally limited to 32 megabytes in size, how do miners make money on bitcoin. The block size limit of one megabyte was introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2010. Eventually the block size limit of one megabyte created problems for transaction processing, such as how do miners make money on bitcoin transaction fees and delayed processing of transactions.[30]Andreas Antonopoulos has stated Lightning Network is a potential scaling solution and referred to lightning as a second-layer routing network.[6]: ch. 8
Ownership

In the blockchain, bitcoins are registered to bitcoin addresses. Creating a bitcoin address requires nothing more than picking a random valid private key and computing the corresponding bitcoin address. This computation can be done in a split second. But the reverse, computing the private key of a given bitcoin address, is practically unfeasible.[6]: ch. 4 Users can tell others or make public a bitcoin address without compromising its corresponding private key. Moreover, the number of valid private keys is so vast that it is extremely unlikely someone will compute a key-pair that is already in use and has funds. The vast number of valid private keys makes it unfeasible that brute force could be used to compromise a private key. To be able to spend their bitcoins, how do miners make money on bitcoin, the owner must know the corresponding private key and digitally sign the transaction.[d] The network verifies the signature using the public key; the private key is never revealed.[6]: ch. 5
If the private key is lost, the bitcoin network will not recognize any other evidence of ownership;[27] the coins are then unusable, and effectively lost. For example, in 2013 one user claimed to have lost 7,500 bitcoins, worth $7.5 million at the time, when he accidentally discarded a hard drive containing his private key.[33] About 20% of all bitcoins are believed to be lost -they would have had a market value of about $20 billion at July 2018 prices.[34]
To ensure the security of bitcoins, the private key must be kept secret.[6]: ch. 10 If the private key is revealed to a third party, e.g. through a data breach, the third party can use it to steal any associated bitcoins.[35] As of December 2017[update], around 980,000 bitcoins have been stolen from cryptocurrency exchanges.[36]
Regarding ownership distribution, as of 16 March 2018, 0.5% of bitcoin wallets own 87% of all bitcoins ever mined.[37]
Mining
See also: Bitcoin network § Mining
Mining is a record-keeping service done through the use of computer processing power.[f] Miners keep the blockchain consistent, complete, and unalterable by repeatedly grouping newly broadcast transactions into a block, which how do miners make money on bitcoin then broadcast to the network and verified by recipient nodes.[26] Each block contains a SHA-256cryptographic hash of the previous block,[26] thus linking it to the previous block and giving the blockchain its name.[6]: ch. 7 [26]
To be accepted by the rest of the network, a new block must contain a proof-of-work (PoW).[26][g] The PoW requires miners to find a number called a nonce (number used once), such that when the block content is hashed along with the nonce, the result is numerically smaller than the network's difficulty target.[6]: ch. 8 This proof is easy for any node in the network to verify, but extremely time-consuming to generate, as for a secure cryptographic hash, miners must try many different nonce values (usually the sequence of tested values is the ascending natural numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3. .) before a result happens to be less than the difficulty target. Because the difficulty target is extremely small compared to a typical SHA-256 hash, block hashes have many leading zeros[6]: ch. 8 as can be seen in this example block hash:
- 0000000000000000000590fc0f3eba193a278534220b2b37e9849e1a770ca959
By adjusting this difficulty target, the amount of work needed to generate a block can be changed. Every 2,016 blocks (approximately 14 days given roughly 10 minutes per block), nodes deterministically adjust the difficulty target based on the recent rate of block generation, with the aim of keeping the average time between new blocks at ten minutes. In this way the system automatically adapts to the total amount of mining power on the network.[6]: ch. 8 As of September 2021[update], it takes on average 79 sextillion (79 thousand billion billion) attempts to generate a block hash smaller than the difficulty target.[42] Computations of this magnitude are extremely expensive and utilize specialized hardware.[43]
The proof-of-work system, alongside the chaining of blocks, makes modifications of the blockchain extremely hard, as an attacker must modify all subsequent blocks in order for the modifications how do miners make money on bitcoin one block to be accepted.[44] As new blocks are mined all the time, the difficulty of modifying a block increases as time passes and the number of subsequent blocks (also called confirmations of the given block) increases.[26]
Computing power is often bundled together by a Mining pool to reduce variance in miner income. Individual mining rigs often have to wait for long periods to confirm a block of transactions and receive payment. In a pool, all participating miners get paid every time a participating server solves a block. This payment depends on the amount of work an individual miner contributed to help find that block.[45]
Supply
The successful miner finding the new block is allowed by the rest of the network to collect for themselves all transaction fees from transactions they included in the block, as well as a pre-determined reward of newly osrs zeah money making bitcoins.[46] As of 11 May 2020[update], this reward is currently 6.25 newly created bitcoins per block.[47] To claim this reward, a special transaction called a coinbase is included in the block, with the miner as the payee.[6]: ch. 8 All bitcoins in existence have been created through this type of transaction. The bitcoin protocol specifies that the reward for adding a block will be reduced by half every 210,000 blocks (approximately every how do miners make money on bitcoin years). Eventually, the reward will round down to zero, and the limit of 21 million bitcoins[h] will be reached c. 2140; the record keeping will then be rewarded by transaction fees only.[48]
Decentralization
Bitcoin is decentralized thus:[7]
- Bitcoin does not have a central authority.[7]
- The bitcoin network is peer-to-peer,[10] without central servers.
- The network also has no central storage; the bitcoin ledger is distributed.[49]
- The ledger is public; anybody can store it on a computer.[6]: ch. 1
- There is no single administrator;[7] the ledger is maintained by a network of equally privileged miners.[6]: ch. 1
- Anyone can become a miner.[6]: ch. 1
- The additions to the ledger are maintained through competition. Until a new block is added to the ledger, it is not known which miner will create the block.[6]: ch, how do miners make money on bitcoin. 1
- The issuance of bitcoins is decentralized. They are issued as a reward for the creation of a new block.[46]
- Anybody can create a new bitcoin address (a bitcoin counterpart of a bank account) without needing any approval.[6]: ch. 1
- Anybody can send a transaction to the network without needing any approval; the network merely confirms that the transaction is legitimate.[50]: 32
Conversely, researchers have pointed out at a "trend towards centralization". Although bitcoin can be sent directly from user to user, in practice intermediaries are widely used.[27]: 220–222 Bitcoin miners join large mining pools to minimize the variance of their income.[27]: 215, 219–222 [51]: 3 [52] Because transactions on how do miners make money on bitcoin network are confirmed by miners, decentralization of the network requires that no single miner or mining pool obtains 51% of the hashing power, which would allow them to double-spend coins, prevent certain transactions from being verified and prevent other miners from earning income.[53] As of 2013[update] just six mining pools controlled 75% of overall bitcoin hashing power.[53] In 2014 mining pool Ghash.io obtained 51% hashing power which raised significant controversies about the safety of the network. The pool has voluntarily capped their hashing power at 39.99% and requested other pools to act responsibly for the benefit of the whole network.[54] Around the year 2017, over 70% of the hashing power and 90% of transactions were operating from China.[55]
According to researchers, other parts of the ecosystem are also "controlled by a small set of entities", notably the maintenance of the client software, online wallets and simplified payment verification (SPV) clients.[53]
Privacy high interest rates foreign investment fungibility
Bitcoin is pseudonymous, meaning that funds are not tied to real-world entities but rather bitcoin addresses. Owners of bitcoin addresses are not explicitly identified, but all transactions on the blockchain are public. In addition, transactions can be linked to individuals and companies through "idioms of use" (e.g., transactions that spend coins from multiple inputs indicate that the inputs may have a common owner) and corroborating public transaction data with known information on owners of certain addresses.[56] Additionally, bitcoin exchanges, where bitcoins are traded for traditional currencies, may be required by law to collect personal information.[57] To heighten financial privacy, a new bitcoin address can be generated for each transaction.[58]
Wallets and similar software technically handle all bitcoins as equivalent, establishing the basic level of fungibility. Researchers have pointed out that the history of each bitcoin is registered and publicly available in the blockchain ledger, and that some users may refuse to accept bitcoins coming from controversial transactions, which would harm bitcoin's fungibility.[59] For example, how do miners make money on bitcoin, in 2012, Mt. Gox froze accounts of users who deposited bitcoins that were known to have just been stolen.[60]
Wallets
For broader coverage of this topic, see Cryptocurrency wallet.

Bitcoin Core, a full client
Electrum, a lightweight client
A wallet stores the information necessary to transact bitcoins. While wallets are often described as a place to hold[61] or store bitcoins, due to the nature of the system, bitcoins are inseparable from the blockchain transaction ledger. A wallet is more correctly defined as something how do miners make money on bitcoin "stores the digital credentials for your bitcoin holdings" and allows one to access (and spend) them.[6]: ch. 1, glossary Bitcoin uses public-key cryptography, in which two cryptographic keys, one public and one private, are generated.[62] At its most basic, a wallet is a collection of these keys.
Software wallets
The first wallet program, simply named Bitcoin, and sometimes referred to as the Satoshi client, was released in how do miners make money on bitcoin by Satoshi Nakamoto as open-source software.[10] In version 0.5 the client moved from the wxWidgets user interface toolkit to Qt, and the whole bundle was referred to as Bitcoin-Qt.[63] After the release of version 0.9, the software bundle was renamed Bitcoin Core to distinguish itself from the underlying network.[64][65] Bitcoin Core is, perhaps, the best known implementation or client. Alternative clients (forks of Bitcoin Core) exist, such as Bitcoin XT, Bitcoin Unlimited,[66] and Parity Bitcoin.[67]
There are several modes which wallets can operate in, how do miners make money on bitcoin. They have an inverse relationship with regards to trustlessness and computational requirements.
- Full clients verify transactions directly by downloading a full copy of the blockchain (over 150 GB as of January 2018[update]).[68] They are the most secure and reliable way of using the network, as trust in external parties is not required. Full clients check the validity of mined blocks, preventing them from transacting on a chain that breaks or alters network rules.[6]: ch. 1 Because of its size and complexity, downloading and verifying the entire blockchain is not suitable for all computing devices.
- Lightweight clients consult full nodes to send and receive transactions without requiring a local copy of the entire blockchain (see simplified payment verification – SPV), how do miners make money on bitcoin. This makes lightweight clients much faster to set up and allows them to be used on low-power, low-bandwidth devices such as smartphones. When using a lightweight wallet, however, the user must trust full nodes, as it can report faulty values back to the user. Lightweight clients follow the longest blockchain and do not ensure it is valid, requiring trust in full nodes.[69]
Third-party internet services called online wallets or webwallets offer similar functionality but may be easier to use. In this case, credentials to access funds are stored with the online wallet provider rather than on the user's hardware.[70] As a result, the user must have complete trust in the online wallet provider. A malicious provider or how do miners make money on bitcoin breach in server security may cause entrusted bitcoins to be stolen. An example of such a security breach occurred with Mt. Gox in 2011.[71]
Cold storage

A paper wallet with the address visible for adding or checking stored funds. The part of the page containing the private key is folded over and sealed.

A hardware wallet peripheral which processes bitcoin payments without exposing any credentials to the computer.
Wallet software is targeted by hackers because of the lucrative potential for stealing bitcoins.[35] A technique called "cold storage" keeps private keys out of reach of hackers; this is accomplished by keeping private keys offline at all times[72][6]: ch. 4 by generating them on a device that is not connected to the internet.[73]: 39 The credentials necessary to spend bitcoins can be stored offline in a number of different ways, from specialized hardware wallets to simple paper printouts of the private key.[6]: ch. 10
Hardware wallets
A hardware wallet is a computer peripheral that signs transactions as requested by the user. These devices store private keys and carry out signing and encryption internally,[72] and do not share any sensitive information with the host computer except already signed (and thus unalterable) transactions.[74] Because hardware wallets never expose withholding investments in energy only markets private keys, even computers that may be compromised by malware do not have a vector to access or steal them.[73]: 42–45
The user sets a passcode when setting up a hardware wallet.[72] As hardware wallets are tamper-resistant,[74][6]: ch. 10 the passcode will be needed to extract how do miners make money on bitcoin money.[74]
Paper wallets
A paper wallet is created with a keypair generated on a computer with no internet connection; the private key is written or printed onto the paper[i] and then erased from the computer.[6]: ch. 4 The paper wallet can then be stored in a safe physical location for later retrieval.[73]: 39
Physical wallets can also take the form of metal token coins[75] with a private key accessible under a security hologram in a recess struck on the reverse side.[76]: 38 The security hologram self-destructs when removed from the token, showing that the private key has been accessed.[77] Originally, these tokens were struck in brass and other base metals, but later used precious metals as bitcoin grew in value and popularity.[76]: 80 Coins with stored face value as high how do miners make money on bitcoin ₿1000 have been struck in gold.[76]: 102–104 The British Museum's coin collection includes four specimens from the earliest series[76]: 83 of funded bitcoin tokens; one is currently on display in the museum's money gallery.[78] In 2013, a Utah manufacturer of these tokens was ordered by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) to register as a money services business before producing any more funded bitcoin tokens.[75][76]: 80
History
Main article: History of bitcoin
Creation
The domain name bitcoin.org was registered on 18 August 2008.[79] On 31 October 2008, a link to a paper authored by Satoshi Nakamoto titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[4] was posted to a cryptography mailing list.[80] Nakamoto implemented the bitcoin software as open-source code and released it in January 2009.[81][82][10] Nakamoto's identity remains unknown.[9]
On 3 January 2009, the bitcoin network was created when Nakamoto mined the starting block of the chain, known as the genesis block.[83][84] Embedded in the coinbase of this block was the text "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks".[10] This note references a headline published by The Times and has been interpreted as both a timestamp and a comment on the instability caused by fractional-reserve banking.[85]: 18
The receiver of stocks to invest in tomorrow first bitcoin transaction was Hal Finney, who had created the first reusable proof-of-work system (RPoW) in 2004.[86] Finney downloaded the bitcoin software on its release date, and on 12 January 2009 received ten bitcoins from Nakamoto.[87][88] Other early cypherpunk supporters were creators of bitcoin predecessors: Wei Dai, creator of b-money, and Nick Szabo, creator of bit gold.[83] In 2010, the first known commercial transaction using bitcoin occurred when programmer Laszlo Hanyecz bought two Papa John's pizzas for ₿10,000 from Jeremy Sturdivant.[89][91][92][93]
Blockchain analysts estimate that Nakamoto had mined about one million bitcoins[94] before disappearing in 2010 when he handed the network alert key and control of the code repository over to Gavin Andresen. Andresen later became lead developer at the Bitcoin Foundation.[95][96] Andresen then sought to decentralize control. This left opportunity for controversy to develop over the future development path of bitcoin, in contrast to the perceived authority of Nakamoto's contributions.[66][96]
2011–2012
After early "proof-of-concept" transactions, the first major users of bitcoin were black markets, such as Silk Road. During its 30 months of existence, beginning in February 2011, Silk Road exclusively accepted bitcoins as payment, transacting 9.9 million in bitcoins, worth about $214 million.[27]: 222
In 2011, the price started at $0.30 per bitcoin, growing to $5.27 for the year. The price rose to $31.50 on 8 June. Within a month, the price fell to $11.00. The next month it fell to $7.80, and in another month to $4.77.[97]
In 2012, bitcoin prices started at $5.27, growing to $13.30 for the year.[97] By 9 January the price had risen to $7.38, but then crashed microtask earn money 49% to $3.80 over the next 16 days. The price then rose to $16.41 on 17 August, but fell by 57% to $7.10 over the next three days.[98]
The Bitcoin Foundation was founded in September 2012 to promote bitcoin's development and uptake.[99]
On 1 November 2011, the reference implementation Bitcoin-Qt version 0.5.0 was released. It introduced a front end that used the Qt user interface toolkit.[100] The software previously used Berkeley DB for database management. Developers switched to LevelDB in release 0.8 in order to reduce blockchain synchronization time.[citation needed] The update to this release resulted in a minor blockchain fork on 11 March 2013. The fork was resolved shortly afterwards.[citation needed] Seeding nodes through IRC was discontinued in how do miners make money on bitcoin 0.8.2. From version 0.9.0 the software was renamed to Bitcoin Core. Transaction fees were reduced again by a factor of ten as a means to encourage microtransactions.[citation needed] Although Bitcoin Core does not use OpenSSL for the operation of the network, the software did use OpenSSL for remote procedure calls. Version 0.9.1 institutional investor money flow released to remove the network's vulnerability to the Heartbleed bug.[citation needed]
2013–2016
In 2013, prices started at $13.30 rising to $770 by 1 January 2014.[97]
In March 2013 the blockchain temporarily split into two independent chains with different rules due to a bug in version 0.8 of the bitcoin software. The two blockchains operated simultaneously for six hours, each with its own version of the transaction history from the moment of the split. Normal operation was restored when the majority of the network downgraded to version 0.7 of the bitcoin software, selecting the backwards-compatible version of the blockchain. As a result, this blockchain became the longest chain and could be accepted by all participants, regardless of their bitcoin software version.[101] During the split, the Mt. Gox exchange briefly halted bitcoin deposits and the price dropped by 23% to $37[101][102] before recovering to the previous level of approximately $48 in the following hours.[103]
The US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) established regulatory guidelines for "decentralized virtual currencies" such as bitcoin, classifying American bitcoin miners who sell their generated bitcoins as Money Service Businesses (MSBs), that are subject to registration or other legal obligations.[104][106]
In April, exchanges BitInstant and Mt. Gox experienced processing delays due to insufficient capacity[107] resulting in the bitcoin price dropping from $266 to $76 before returning to $160 within six hours.[108] The bitcoin price rose to $259 on 10 April, how do miners make money on bitcoin, but then crashed by 83% to $45 over the next three days.[98]
On 15 May 2013, how do miners make money on bitcoin, US authorities seized accounts associated with Mt. Gox after discovering it had not registered as a money how do miners make money on bitcoin with FinCEN in the US.[109][110] On 23 June 2013, the US Drug Enforcement Administration listed ₿11.02 as a seized asset in a United States Department of Justice seizure notice pursuant to 21 U.S.C. § 881. This marked the first time a government agency had seized bitcoin.[111] The FBI seized about ₿30,000[112] in October 2013 from the dark web website Silk Road, following the arrest of Ross William Ulbricht.[113][114][115] These bitcoins were sold at blind auction by the United States Marshals Service to venture capital investor Tim Draper.[112] Bitcoin's price rose to $755 on 19 November and crashed by 50% to $378 the same day. On 30 November 2013, the price reached $1,163 before starting a long-term crash, declining by 87% to $152 in January 2015.[98]
On 5 December 2013, the People's Bank of China prohibited Chinese financial institutions from using bitcoins.[116] After the announcement, the value of bitcoins dropped,[117] and Baidu no making money raising cattle accepted bitcoins for certain services.[118] Buying real-world goods with any virtual currency had been illegal in China since at least 2009.[119]
In 2014, prices started at $770 and fell to $314 for the year.[97] On 30 July 2014, the Wikimedia Foundation started accepting donations of bitcoin.[120]
In 2015, prices started at $314 and rose to $434 for the year. In 2016, prices rose and climbed up to $998 by 1 January 2017.[97]
Release 0.10 of the software was made public on 16 February 2015. It introduced a consensus library which gave programmers easy access to the rules governing consensus on the network. In version 0.11.2 developers added a new feature which allowed transactions to be made unspendable until a specific time in the future.[121] Bitcoin Core 0.12.1 was released on 15 April 2016, and enabled multiple soft forks to occur concurrently.[122] Around 100 contributors worked on Bitcoin Core 0.13.0 which was released on 23 August 2016, how do miners make money on bitcoin.
In July 2016, the CheckSequenceVerify soft fork activated.[123] In August 2016, the Bitfinex cryptocurrency exchange platform was hacked in the second-largest breach of a Bitcoin exchange platform up to that time, and 119,756 bitcoin,[124] worth about $72 million at the time, were stolen.[125]
In October 2016, Bitcoin Core's 0.13.1 release featured the "Segwit" soft fork that included a scaling improvement aiming to optimize the bitcoin blocksize.[citation needed] The patch which was originally finalised in April, and 35 developers were engaged to deploy it.[citation needed] This release featured Segregated Witness (SegWit) which aimed to place downward pressure on transaction fees as well as selling photos online to make money the maximum transaction capacity of the network.[126][non-primary source needed] The 0.13.1 release endured extensive testing and research leading to some delays in its release date.[citation needed] SegWit prevents various forms of transaction malleability.[127][non-primary source needed]
2017–2019
Research produced by the University of Cambridge estimated that in 2017, there were 2.9 to 5.8 million unique users using a cryptocurrency wallet, how do miners make money on bitcoin, most of them using bitcoin.[128] On 15 July 2017, how do miners make money on bitcoin, the controversial Segregated Witness [SegWit] software upgrade was approved ("locked-in"). Segwit was intended to support the Lightning Network as well as improve scalability.[129] SegWit was subsequently activated on the network on 24 August 2017, how do miners make money on bitcoin. The bitcoin price rose almost 50% in the week following SegWit's approval.[129] On 21 July 2017, bitcoin was trading at $2,748, up 52% from 14 July 2017's $1,835.[129] Supporters of large blocks who were dissatisfied with the activation of SegWit forked the software on 1 August 2017 to create Bitcoin Cash, becoming one of many forks of bitcoin such as Bitcoin Gold.[130]
Prices started at $998 in 2017 and rose to $13,412.44 on 1 January 2018,[97] after reaching its all-time high of $19,783.06 on 17 December 2017.[131]
China banned trading in bitcoin, with first steps taken in September 2017, and a complete ban that started on 1 February 2018. Bitcoin prices then fell from $9,052 to $6,914 on 5 February 2018.[98] The percentage of bitcoin trading in the Chinese renminbi fell from over 90% in September 2017 to less than 1% in June 2018.[132]
Throughout the rest of the first half of 2018, bitcoin's price fluctuated between $11,480 and $5,848. On 1 July 2018, how do miners make money on bitcoin, bitcoin's price was $6,343.[133][134] The price on 1 January 2019 was $3,747, how do miners make money on bitcoin, down 72% for 2018 and how do miners make money on bitcoin 81% since the all-time high.[133][135]
In September 2018, an anonymous party discovered and reported an invalid-block denial-of-server vulnerability to developers of Bitcoin Core, Bitcoin ABC and Bitcoin Unlimited. Further analysis by bitcoin developers showed the issue could also allow the creation of blocks violating the 21 million coin limit and CVE-2018-17144 was assigned and the issue resolved.[136][non-primary source needed]
Bitcoin prices were negatively affected by several hacks or thefts from cryptocurrency exchanges, including thefts from Coincheck in January 2018, Bithumb in June, and Bancor in July. For the first six months of 2018, $761 million worth of cryptocurrencies was reported stolen from exchanges.[137] Bitcoin's price was affected even though other cryptocurrencies were stolen at Coinrail and Bancor as investors worried about the security of cryptocurrency exchanges.[138][139][140] In September 2019 the Intercontinental Exchange (the owner of the NYSE) began trading of bitcoin futures on its exchange called Bakkt.[141] Bakkt also announced that it would launch options on bitcoin in December 2019.[142] In December 2019, YouTube removed bitcoin and cryptocurrency videos, but later restored the content after judging they had "made the wrong call."[143]
In February 2019, how do miners make money on bitcoin, Canadian cryptocurrency exchange Quadriga Fintech Solutions failed with approximately $200 million missing.[144] By June 2019 the price had recovered to $13,000.[145]
2020–present

On 13 March 2020, bitcoin fell below $4,000 during a broad market selloff, after trading above $10,000 in February 2020.[146] On 11 March 2020, 281,000 bitcoins were sold, held by owners for only thirty days.[145] This compared to ₿4,131 that had laid dormant for a year or more, indicating that the vast majority of the bitcoin volatility on that day was from recent buyers. During the week of 11 March 2020, cryptocurrency exchange Kraken experienced an 83% increase in the number of account signups over the week of bitcoin's price collapse, a result of buyers looking to capitalize on the low price.[145] These events were attributed to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In August 2020, how do miners make money on bitcoin, MicroStrategy invested $250 million in bitcoin as a treasury reserve asset.[147] In October 2020, Square, Inc. placed approximately 1% of total assets ($50 million) in bitcoin.[148] In November 2020, PayPal announced that US users could buy, hold, or sell bitcoin.[149] On 30 November how do miners make money on bitcoin, the bitcoin value reached a new all-time high of $19,860, topping the previous high of December 2017.[150]Alexander Vinnik, founder of BTC-e, was convicted and sentenced to five years in prison for money laundering in France while refusing to testify during his trial.[151] In December 2020 Massachusetts Mutual Life Insurance Company announced a bitcoin purchase of US$100 million, or roughly 0.04% of its general investment account.[152]
On 19 January 2021, Elon Musk placed the handle #Bitcoin in his Twitter profile, tweeting "In retrospect, it was inevitable", how do miners make money on bitcoin, which caused the price to briefly rise about $5000 in an hour to $37,299.[153] On 25 January 2021, Microstrategy announced that it continued to buy bitcoin and as of the same date it had holdings of ₿70,784 worth $2.38 billion.[154] On 8 February 2021 Tesla's announcement of a bitcoin purchase of US$1.5 billion and the plan how do miners make money on bitcoin start accepting bitcoin as payment for vehicles, pushed the bitcoin price to $44,141.[155] On 18 February 2021, Elon Musk stated that "owning bitcoin was only a little better than holding conventional cash, but that the slight difference made it a better asset to hold".[156] After 49 days of accepting the digital currency, Tesla reversed course on 12 May 2021, saying they would no longer take Bitcoin due to concerns that "mining" the cryptocurrency was contributing to the consumption of fossil fuels and climate change.[157] The decision resulted in the price of Bitcoin dropping around 12% on 13 May.[158] During a July Bitcoin conference, Musk suggested Tesla could possibly help Bitcoin miners switch to renewable energy in the future and also stated at the same conference that if Bitcoin mining reaches, and trends above 50 percent renewable energy usage, that "Tesla would resume accepting bitcoin." The price for bitcoin rose after this announcement.[159]
In June 2021, the Legislative Assembly of El Salvador voted legislation to make Bitcoin legal tender in El Salvador.[j][168][163][169] The law took effect on 7 September.[170][8] How do miners make money on bitcoin implementation of the law has been met with protests[171] and calls to make the currency optional, not compulsory.[172] According to a survey by the Central American University, the majority of Salvadorans disagreed with using cryptocurrency as a legal tender,[173][174] and a survey by the Center for Citizen Studies (CEC) showed that 91% of the country prefers the dollar over Bitcoin.[175] As of October 2021, the country's government was exploring mining bitcoin with geothermal power and issuing bonds tied to bitcoin.[176] According to a survey done by the Central American University 100 days after the Bitcoin Law came into force: 34.8% of the population has no confidence in Bitcoin, 35.3% has little confidence, 13.2% has some confidence, and 14.1% has a how much money have you made bitcoin mining of confidence. 56.6% of respondents have downloaded the government Bitcoin wallet; among them 62.9% has never used it or only once whereas 36.3% uses Bitcoin at least once a month.[177][178] In 2022, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) urged El Salvador to reverse its decision after Bitcoin lost half its value in two months. The IMF also warned that it would be difficult to get a loan from the institution.[179]
Also In June, the Taproot apps to have when investing into bitcoin software upgrade was approved, adding support for Schnorr signatures, improved functionality of Smart contracts and Lightning Network.[180] The upgrade was installed in November.[181]
On 16 October 2021, the SEC approved the ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF, a cash-settled futuresexchange-traded fund (ETF). The first bitcoin ETF in the United States gained 5% on its first trading day on 19 October 2021.[182][183]
Associated ideologies
Satoshi Nakamoto stated in an essay accompanying bitcoin's code that: "The root problem with conventional currencies is all the trust that's required to make it work. The central bank must be trusted not to debase the currency, but the history of fiat currencies is full of breaches of that trust."[184]
Austrian economics roots
According to how do miners make money on bitcoin European Central Bank, how do miners make money on bitcoin, the decentralization of money offered by bitcoin has its theoretical roots in the Austrian school of economics, especially with Friedrich von Hayek in his book Denationalisation of Money: The Argument Refined,[185] in which Hayek advocates a complete free market in the production, distribution and management of money to end the monopoly of central banks.[186]: 22
Anarchism and libertarianism
Further information: Crypto-anarchism
According to The New York Times, libertarians and anarchists were attracted to the philosophical idea behind bitcoin. Early bitcoin supporter Roger Ver said: "At first, almost everyone who got involved did so for philosophical reasons. We saw bitcoin as a great idea, as a way to separate money from the state."[184]The Economist describes bitcoin as "a techno-anarchist project to create an online version of cash, a way for people to transact without the possibility of interference from malicious governments or banks".[187] Economist Paul Krugman argues that cryptocurrencies like bitcoin are "something of a cult" based in "paranoid fantasies" of government power.[188]
Nigel Dodd argues in The Social Life of Bitcoin that the essence of the bitcoin ideology is to remove money from social, as well as governmental, control.[190] Dodd quotes a YouTube video, with Roger Ver, Jeff Berwick, Charlie Shrem, Andreas Antonopoulos, Gavin Wood, Trace Meyer and other proponents of bitcoin reading The Declaration of Bitcoin's Independence. The declaration includes a message of crypto-anarchism with the words: "Bitcoin is inherently anti-establishment, anti-system, and anti-state. Bitcoin undermines governments and disrupts institutions because bitcoin is fundamentally humanitarian."[190][189]
David Golumbia says that the ideas influencing bitcoin advocates emerge from right-wing extremist movements such as the Liberty Lobby and the John Birch Society and their anti-Central Bank rhetoric, or, more recently, Ron Paul and Tea Party-style libertarianism.[191]Steve Bannon, who owns a "good stake" in bitcoin, considers it to be "disruptive populism. It takes control back from central authorities. It's revolutionary."[192]
A 2014 study of Google Trends data found correlations between bitcoin-related searches and ones related to computer programming and illegal activity, but not libertarianism or investment topics.[193]
Economics
Main article: Economics of bitcoin
Bitcoin is a digital asset designed to work in peer-to-peer transactions as a currency.[4][194] Bitcoins have three qualities useful in a currency, according to The Economist in January 2015: they are "hard to earn, limited in supply and easy to verify."[195] Per some researchers, as of 2015[update], bitcoin functions more as a payment system than as a currency.[27]
Economists define money as serving the following three purposes: a store of value, a medium of exchange, and a unit of account.[196] According to The Economist in 2014, bitcoin functions best as a medium of exchange.[196] However, this is debated, and a 2018 assessment by The Economist stated that cryptocurrencies met none of these three criteria.[187] Yale economist Robert J. Shiller writes that bitcoin has potential as a unit of account for measuring the relative value of goods, as with Chile's Unidad de Fomento, but that "Bitcoin in its present form [.] doesn't really solve any sensible economic problem".[197]
According to research by Cambridge University, between 2.9 million and 5.8 million unique users used a cryptocurrency wallet in 2017, most of them for bitcoin. The number of users has grown significantly since 2013, when there were 300,000–1.3 million users.[128]
Acceptance by merchants
The overwhelming majority of bitcoin transactions take place on a cryptocurrency exchange, rather than being used in transactions with merchants.[198] Delays processing payments through the blockchain of about ten minutes make bitcoin use very difficult in a retail setting. Prices are not usually quoted in units of bitcoin and many trades involve one, how do miners make money on bitcoin, or sometimes two, conversions into conventional currencies.[27] Merchants that do accept bitcoin payments may use payment service providers to perform the conversions.[199]
In 2017 and 2018 bitcoin's acceptance among major online retailers included only three of the top 500 U.S. online merchants, down from five in 2016.[198] Reasons for this decline include high transaction fees due to bitcoin's scalability issues and long transaction times.[200]
Bloomberg reported that the largest 17 crypto merchant-processing services handled $69 million in June 2018, down from $411 million in September 2017. How do miners make money on bitcoin is "not actually usable" for retail transactions because of high costs and the inability to process chargebacks, according to Nicholas Weaver, a researcher quoted by Bloomberg. High price volatility and transaction fees make paying for small retail purchases with bitcoin impractical, according to economist Kim Grauer. However, bitcoin continues to be used for large-item purchases on sites such as Overstock.com, and for cross-border payments to freelancers and other vendors.[201]
Financial institutions
Bitcoins can be bought on digital currency exchanges.
Per researchers, "there is little sign of bitcoin use" in international remittances despite high fees charged by banks and Western Union who compete in this market.[27] The South China Morning Post, however, mentions the use of bitcoin by Hong Kong workers to transfer money home.[202]
In 2014, the National Australia Bank closed accounts of businesses with ties to bitcoin,[203] and HSBC refused to serve a hedge fund with links to bitcoin.[204] Australian banks in general have been reported as closing down bank accounts of operators of businesses involving the currency.[205]
On 10 December 2017, the Chicago Board Options Exchange started trading bitcoin futures,[206] followed by the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, which started trading bitcoin futures on 17 December 2017.[207]
In September 2019 the Central Bank of Venezuela, at the request of PDVSA, ran tests to determine if bitcoin and ether could be held in central bank's reserves. The request was motivated by oil company's goal to pay its suppliers.[208]
François R. Velde, Senior Economist at the Chicago Fed, described bitcoin as "an elegant solution to the problem of creating a digital currency".[209] David Andolfatto, Vice President at the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, stated that bitcoin is a threat to the establishment, which he argues is a good thing for the Federal Reserve System and other central banks, because it prompts these institutions to operate sound policies.[40]: 33 [210][211]
As an investment
The Winklevoss twins have purchased bitcoin. In 2013, The Washington Post reported a claim that they owned 1% of all the bitcoins in existence at the time.[212]
Other methods of investment are bitcoin funds. The first regulated bitcoin fund was established in Jersey in July 2014 and approved by the Jersey Financial Services Commission.[213]
Forbes named bitcoin the best investment of 2013.[214] In 2014, Bloomberg named bitcoin one of its worst investments of the year.[215] In 2015, bitcoin topped Bloomberg's currency tables.[216]
According to bitinfocharts.com, in 2017, there were 9,272 bitcoin wallets with more than $1 million worth of bitcoins.[217] The exact number of bitcoin millionaires is uncertain as a single person can have more than one bitcoin wallet.
Venture capital
Peter Thiel's Founders Fund invested US$3 million in BitPay.[218] In 2012, an incubator for bitcoin-focused start-ups was founded by Adam Draper, with financing help from his father, venture capitalist Tim Draper, one of the largest bitcoin investimento wallet holders after winning an auction of 30,000 bitcoins,[219] at the time called "mystery buyer".[220] The company's goal is to fund 100 bitcoin businesses within 2–3 years with $10,000 to $20,000 for a 6% stake.[219] Investors also invest in bitcoin mining.[221] According to a 2015 study by Paolo Tasca, bitcoin startups raised almost $1 billion in three years (Q1 2012 – Q1 2015).[222]
Price and volatility
The price of bitcoins has gone through cycles of appreciation and depreciation referred to by some as bubbles and busts.[223] In 2011, the value of one bitcoin rapidly rose from about US$0.30 to US$32 before returning to US$2.[224] In the latter half of 2012 and during the 2012–13 Cypriot financial crisis, the bitcoin price began to rise,[225] reaching a high of US$266 on 10 April 2013, before crashing to around US$50. On 29 November 2013, the cost of one bitcoin rose to a peak of US$1,242.[226] In 2014, the price fell sharply, and as of April remained depressed bitcoin investor seriö s rights little more than half 2013 prices. As of August 2014[update] it was under US$600.[227]
According to Mark T. Williams, as of 30 September 2014[update], bitcoin has volatility seven times greater than gold, eight times greater than the S&P 500, and 18 times greater than the US dollar.[228] Hodl is a meme created in reference to holding (as opposed to selling) during periods of volatility. Unusual for an asset, bitcoin weekend trading during December 2020 was higher than for weekdays.[229]Hedge funds (using high leverage and derivates)[230] have attempted to use the volatility to profit from downward price movements. At the end of January 2021, how do miners make money on bitcoin, such positions were over $1 billion, their highest of all time.[231] As of 8 February 2021[update], the closing price of bitcoin equaled US$44,797.[232]
Legal status, tax and regulation
Further information: Legality of bitcoin by country or territory
Because of bitcoin's decentralized nature and its trading on online exchanges located in many countries, regulation of bitcoin has been difficult. However, the use of bitcoin can be criminalized, and shutting down exchanges and the peer-to-peer economy in a given country would constitute a de facto ban.[233] The legal status of bitcoin varies substantially from country to country and is still undefined or changing in many of them. Regulations and bans that apply to bitcoin probably extend to similar cryptocurrency systems.[222]
According to iphone apps that can earn you money Library of Congress, an "absolute ban" on trading or using cryptocurrencies applies in nine countries: Algeria, Bolivia, Egypt, Iraq, Morocco, Nepal, Pakistan, Vietnam, and the United Arab Emirates. An "implicit ban" applies in another 15 countries, which include Bahrain, Bangladesh, China, Colombia, the Dominican Republic, Indonesia, Kuwait, Lesotho, Lithuania, Macau, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and Taiwan.[234]
Regulatory warnings
The U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission has issued four "Customer Advisories" for bitcoin and related investments.[12] A July 2018 warning emphasized that trading in any cryptocurrency is often speculative, and there is a risk of theft from hacking, and fraud.[235] In May 2014 the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission warned that investments involving bitcoin might have high rates of fraud, and that investors might be solicited on social media sites.[236] An earlier "Investor Alert" warned about the use of bitcoin in Ponzi schemes.[237]
The European Banking Authority issued a warning in 2013 focusing on the lack of regulation of bitcoin, the chance that exchanges would be hacked, the volatility of bitcoin's price, and general fraud.[238]FINRA and the North American Securities Administrators Association have both issued investor alerts about bitcoin.[239][240]
Price manipulation investigation
An official investigation into bitcoin traders was reported in May 2018.[241] The U.S. Justice Department launched an investigation into possible price manipulation, including the techniques of spoofing and wash trades.[242][243][244]
The U.S. federal investigation was prompted by concerns of possible manipulation during futures settlement dates. The final settlement price of CME bitcoin futures is determined by prices on four exchanges, Bitstamp, Coinbase, itBit and Kraken. Following the first delivery date in January 2018, the CME requested extensive detailed trading information but several of the exchanges refused to provide it and later provided only limited data. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission then subpoenaed the data from the exchanges.[245][246]
State and provincial securities regulators, coordinated through the North American Securities Administrators Association, are investigating "bitcoin scams" and ICOs in 40 jurisdictions.[247]
Academic research published in the Journal of Monetary Economics concluded that price manipulation occurred during the Mt Gox bitcoin theft and that the market remains vulnerable to manipulation.[248] The history of hacks, how do miners make money on bitcoin, fraud and theft involving bitcoin dates back to at least 2011.[249]
Research by John M. Griffin and Amin Shams in 2018 suggests that trading associated with increases in the amount how do miners make money on bitcoin the Tether cryptocurrency and associated trading at the Bitfinex exchange account for about half of the price increase in bitcoin in late 2017.[250][251]
J.L. van der Velde, CEO of both Bitfinex and Tether, denied the claims of price manipulation: "Bitfinex nor Tether is, or has ever, engaged in any sort of market or price manipulation. Tether issuances cannot be used to prop up the price of bitcoin or any where to invest now in stocks coin/token on Bitfinex."[252]
Adoption by governments
El Salvador officially adopted Bitcoin as legal tender, in the face of internal and international criticism, becoming the first nation to do so.[253]
Iran announced pending regulations that would require bitcoin miners in How do miners make money on bitcoin to sell bitcoin to the Central Bank of Iran, and the central bank would use it for imports.[254] Iran, as of October 2020, had issued over 1,000 bitcoin mining licenses.[254] The Iranian government initially took a stance against cryptocurrency, but later changed it after seeing that digital currency could be used to circumvent sanctions.[255] The US Office of Foreign Assets Control listed two Iranians and their bitcoin addresses as part of its Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons List for their role in the 2018 Atlanta cyberattack whose ransom was paid in bitcoin.[256]
In Switzerland, the Canton of Zug accepts tax payments in bitcoin.[257][258]
Criticisms
Economic concerns
Further information: Cryptocurrency bubble and Economics of bitcoin
Bitcoin, along with other cryptocurrencies, has been described as an economic bubble by at least eight Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences laureates at various times, including Robert Shiller on 1 March 2014,[197]Joseph Stiglitz on 29 November 2017,[259] and Richard Thaler on 21 December 2017.[260][261] On 29 January 2018, a noted Keynesian economist Paul Krugman has described bitcoin as "a bubble wrapped in techno-mysticism inside a cocoon of libertarian ideology",[188] on 2 February 2018, professor Nouriel Roubini of New York University has called bitcoin the "mother of all bubbles",[262] and on 27 April 2018, a University of Chicago economist James Heckman has compared it to the 17th-century tulip mania.[261]
Journalists, economists, investors, and the central bank of Estonia have voiced concerns that bitcoin is a Ponzi scheme.[263][264][265][266] In April 2013, Eric Posner, a law professor at the University of Chicago, stated that "a real Ponzi scheme takes fraud; is today a good day to invest in the stock market, by contrast, seems more like a collective delusion."[267] A July 2014 report by the World Bank concluded that bitcoin was not a deliberate Ponzi scheme.[268]: 7 In June 2014, the Swiss Federal Council examined concerns that bitcoin might be a pyramid scheme, and concluded that "since in the case of bitcoin the typical promises of profits are lacking, it cannot be assumed that bitcoin is a pyramid scheme."[269]: 21
Bitcoin wealth is highly concentrated, with 0.01% holding 27% of in-circulation currency, as of 2021.[270]
Energy consumption and carbon footprint
Main article: Environmental impact of cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin has been criticized for the amount of electricity consumed by mining.[271]
As of 2022[update], the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance (CCAF) estimates that bitcoin consumes 131 TWh annually, representing 0.29% of the world's energy production and ranking bitcoin mining between Ukraine and Egypt in terms of electricity consumption.[272][273]
Until 2021, according to the CCAF much of bitcoin mining was done in China.[274][275] Chinese miners used to rely on cheap coal power in Xinjiang[276][277] in late autumn, how do miners make money on bitcoin, winter and spring, and then migrate to regions with overcapacities in low-cost hydropower, like Sichuan, between May and October. In June 2021 China banned Bitcoin mining[278] and Chinese miners moved to other countries such as the US and Kazakhstan.[279]
As of September 2021, according to the New York Times, Bitcoin's use of renewables range from 40% to 75%.[271] According to the Bitcoin Mining Council and based on a survey of 32% of the current global bitcoin network, 56% of bitcoin mining came from renewable resources in Q2 2021.[280]
The development of intermittent renewable energy sources, such as wind power and solar power, is challenging because they cause instability in the electrical grid. Several papers concluded that these renewable power stations could use the surplus energy to mine Bitcoin and thereby reduce curtailment, hedgeelectricity price risk, stabilize the grid, increase the profitability of renewable energy infrastructure, and therefore accelerate transition to sustainable energy and decrease Bitcoin's carbon footprint.[281][282][283][284][285][286][287][288]
Concerns about bitcoin's environmental impact relate bitcoin's energy consumption to carbon emissions.[289][290] The difficulty of translating the energy consumption into carbon emissions lies in the decentralized nature of bitcoin impeding the localization of miners to examine the electricity mix used. The results of recent studies analyzing bitcoin's carbon footprint vary.[291][292][293][294] A 2018 study published in Nature Climate Change by Mora et al. claimed that bitcoin "could alone produce enough CO2 emissions to push warming above 2 °C within less than three decades."[293] However, three other studies also published in Nature Climate Change later dismissed this analysis on account of its poor methodology and false assumptions with one study concluding: "[T]he scenarios used by Mora et al are fundamentally flawed and should not be taken seriously by the public, researchers, how do miners make money on bitcoin, or policymakers."[295][296][297] According to studies published in Joule and American Chemical Society in 2019, bitcoin's annual energy consumption results in electrician or plumber make more money carbon emission ranging from 17[298] to 22.9 MtCO2 which is comparable to the level of emissions of countries as Jordan and Sri Lanka or Kansas City.[294] George Kamiya, how do miners make money on bitcoin, writing for the International Energy Agency, how do miners make money on bitcoin, says that "predictions about bitcoin consuming the entire world's electricity" are sensational, but that the area "requires careful monitoring and rigorous analysis".[299] One study done by Michael Novogratz's Galaxy Digital claimed that Bitcoin mining how do miners make money on bitcoin less energy than the traditional banking system.[300]
Electronic waste
Bitcoins gang members make money e-waste is estimated to be about 30 metric tons as of May 2021, which is comparabe to the small IT equipment waste produced by the Netherlands. One Bitcoin generates 272g of e-waste per transaction. The average lifespan of Bitcoin mining devices is estimated to be only 1.29 years.[301][302] Other estimates assume that a Bitcoin transaction generates about 380g of e-waste, equivalent of 2.35 iPhones.[303] One reason for the e-waste problem of Bitcoin is that unlike most computing hardware the used application-specific integrated circuits have no alternative use beyond Bitcoin mining.[304]
Use in illegal transactions
Further information: Cryptocurrency and crime and Bitcoin network § Alleged criminal activity
The use of bitcoin by criminals has attracted the attention of financial regulators, legislative bodies, law enforcement, and the media.[305]
Several news outlets have asserted that the popularity of bitcoins hinges on the ability to use them to purchase illegal goods.[194][306] Nobel-prize winning economist Joseph Stiglitz says that bitcoin's anonymity encourages money laundering and other crimes.[307][308]
Software implementation
Bitcoin Core is free and open-source software that serves as a bitcoin node (the set of which form the bitcoin network) and provides a bitcoin wallet which fully verifies payments. It is considered to be bitcoin's reference implementation.[309] Initially, the software was published by Satoshi Nakamoto under the name "Bitcoin", and later renamed to "Bitcoin Core" to distinguish it from the network.[310] It is also known as the Satoshi client.[311]
The MIT Digital Currency Initiative funds some of the development of Bitcoin Core.[312] The project also maintains the cryptography library libsecp256k1.[313]
Bitcoin Core includes a transaction verification engine and connects to the bitcoin network as a full node.[311] Moreover, a cryptocurrency wallet, which can be used to transfer funds, how do miners make money on bitcoin, is included by default.[313] The wallet allows for the sending and receiving of bitcoins. It does not facilitate the buying or selling of bitcoin. It allows users to generate QR codes to receive payment.
The software validates the entire blockchain, which includes all bitcoin transactions ever. This distributed ledger which has reached more than 235 gigabytes in size as of Jan 2019, must be downloaded or synchronized before full participation of the client may occur.[311] Although the complete blockchain is not needed all at once since it is possible to run in pruning mode. A command line-based daemon with a JSON-RPC interface, bitcoind, is bundled with Bitcoin Core. It also provides access to testnet, a global testing environment how do miners make money on bitcoin imitates the bitcoin main network using an alternative how do miners make money on bitcoin where valueless "test bitcoins" are used. Regtest or Regression Test Mode creates a private blockchain which is used as a local testing environment.[314] Finally, bitcoin-cli, a simple program which allows users to send RPC commands to bitcoind, is also included.
Checkpoints which have been hard coded into the client are used only to prevent Denial of Service attacks against nodes which are initially syncing the chain. For this reason the checkpoints included are only as of several years ago.[315][316][failed verification] A one megabyte block size limit was added in 2010 by Satoshi Nakamoto. This limited the maximum network capacity to about three transactions per second.[317] Since then, network capacity has been improved incrementally both through block size increases and improved wallet behavior. A network how do miners make money on bitcoin system was included by Satoshi Nakamoto as a way of informing users of important news regarding bitcoin.[318] In November 2016 it was retired. It had become obsolete as news on bitcoin is now widely disseminated.
Bitcoin Core includes a scripting language inspired by Forth that can define transactions and specify parameters.[319] ScriptPubKey is used to "lock" transactions based on a set of future conditions. scriptSig is used to meet these conditions or "unlock" a transaction. Operations on the data are performed by various OP_Codes. Two stacks are used – main and alt. Looping is forbidden.
Bitcoin Core uses OpenTimestamps to timestamp merge commits.[320]
The original creator of the bitcoin client has described their approach to the software's authorship as it being written first to prove to themselves that the concept of purely bitcoin investing for beginners 2022 electronic cash was valid and that a paper with solutions could be written. The lead developer is Wladimir J. van der Laan, who took over the role on 8 April 2014.[321]Gavin Andresen was the former lead maintainer for the software client. Andresen left the role of lead developer for bitcoin to work on the strategic development of its technology.[321] Bitcoin Core in 2015 was central to a dispute with Bitcoin XT, how do miners make money on bitcoin, a competing client that sought to increase the blocksize.[322] Over a dozen different companies and industry groups fund the development of Bitcoin Core.
In popular culture
Term "HODL"
Hodl (HOD-əl; often written HODL) is slang in the cryptocurrency community for holding a cryptocurrency rather than selling it. A person who does this is known as a Hodler. It originated in a December 2013 post on the Bitcoin Forum message board by an apparently inebriated user who posted with a typo in the subject, "I AM HODLING."[323] It is often humorously suggested to be a backronym to "hold on for dear life".[324] In 2017, Quartz listed it as one of the essential slang terms in Bitcoin culture, and described it as a stance, "to stay invested in bitcoin and not to capitulate in the face of plunging prices."[325]TheStreet.com referred to it as the "favorite mantra" of Bitcoin holders.[326]Bloomberg News referred to it as a mantra for holders during market routs.[327]
Literature
In Charles Stross' 2013 science fiction novel, Neptune's Brood, the universal interstellar payment system is known as "bitcoin" and operates using cryptography.[328] Stross later blogged that the reference was intentional, saying "I wrote Neptune's Brood in 2011. Bitcoin was obscure back then, earn a lot of money jobs I figured had just enough name recognition to be a useful term for an interstellar currency: it'd clue people in that it was a networked digital currency."[329]
Film
The 2014 documentary The Rise and Rise of Bitcoin portrays the diversity of motives behind the use of bitcoin by interviewing people who use it. These include a computer programmer and a drug dealer.[330] The 2016 documentary Banking on Bitcoin is an introduction to the beginnings of bitcoin and the ideas behind cryptocurrency today.[331]
Music
In 2018, a Japanese band called Kasotsuka Shojo – Virtual Currency Girls – launched. Each of the eight members represented a cryptocurrency, including Bitcoin, Ethereum and Cardano.[332][333]
Academia
In September 2015, the establishment of the peer-reviewedacademic journalLedger (ISSN 2379-5980) was announced. It covers studies of cryptocurrencies and related technologies, and is published by the University of Pittsburgh.[334] The journal encourages authors to digitally sign a file hash of submitted papers, which will then be timestamped into the bitcoin blockchain. Authors are also asked to include a personal bitcoin address in the first page of their papers.[335][336]
See also
Notes
What Is Bitcoin Mining? How It Works and What It Takes to Make It Pay
Despite the cryptocurrency’s wildly volatile price and the increasing environmental concerns, Bitcoin mining is booming in North America. The state of Texas, in particular, has begun to emerge as an epicenter since China banned the industry in 2021, sparking an exodus of miners from the country. The ban, which reportedly reduced China’s control of Bitcoin mining from about two-thirds of the global industry in April 2021 to zero in July 2021, has created a new opportunity for North American companies, particularly those in the energy industry, to become more familiar with Bitcoin mining and incorporate it into their business models.
For those unfamiliar with Bitcoin’s inner workings, “mining” is how transactions are validated for a blockchain. It’s essentially a cryptographic competition to add blocks, or records, to the cryptocurrency’s ever-expanding blockchain network. In exchange for this service, winning miners are paid in Bitcoin (BTC), which reached a record price of more than $68,000 in November 2021.
In the wake of the Chinese ban, companies based in North America, which include Riot Blockchain and Marathon Digital Holdings, are raising record amounts of capital as they ramp up production and expand their industrial-scale operations. At the same time, Chinese companies have joined what’s been termed the Great Mining Migration to North America, investing in US facilities and constructing their own massive warehouses equipped how do miners make money on bitcoin thousands of small computers designed specifically to mine a number of cryptocurrencies, the most popular how do miners make money on bitcoin which is Bitcoin.
What I’ve learned from my experience conducting feasibility studies for Canada-based clients exploring this booming business is that new entrants, specifically energy companies, are also moving into the sector in a material way through joint ventures and other partnerships. The how do miners make money on bitcoin of power is one of the most significant factors in cryptocurrency mining. That means companies with access to reliable, low-cost electricity—particularly from renewable sources—have an opportunity to play a central role as the industry evolves in North America.
In this article, I offer insights into the fundamentals of Bitcoin mining, and show how to calculate the costs and the rewards, which can be immense. I also address the challenges of the industry, including questions around energy usage and risks, like the ever-evolving crypto regulatory environment.
Bitcoin Is Booming
Bitcoin has inspired thousands of cryptocurrencies since it launched in 2009, but in terms of value, it still stands alone. Despite the volatility of its price, its monetary policy builds in a measure of stability by limiting mining to 21 million Bitcoins across a predefined schedule. Although there are almost 19 million now in circulation, the reward for mining is periodically cut in half so that it will take until 2140 to exhaust production of Bitcoin.
While other crypto networks also manage supply, none have been able to replicate Bitcoin’s popularity. As investors embraced the asset class, Bitcoin’s futures and exchange-traded funds became the first to be introduced in regulated US and European markets. It soon appeared on the balance sheets of companies like Tesla and Overstock. This demand helped push Bitcoin’s market cap past $1 trillion in November 2021. By way of contrast, the second-most-popular cryptocurrency, Ethereum, reached only about half that value.
Bitcoin also stands out because of the industrial-scale mining operations, or farms, it has spawned. The largest crypto facilities with the most advanced technology are focused primarily or exclusively on Bitcoin, like the Genesis Mining farm, which consumes more electricity than any other company in Iceland. One of the biggest farms in North America is Riot Blockchain’s Texas facility, which occupies three large warehouses on 100 how do miners make money on bitcoin of land containing 60,000 mining computers focused only on Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Mining Basics
At the root of every cryptocurrency is a blockchain, which is essentially an electronic ledger sustaining a continuously growing list of records. The blocks in the chain are basically files how do miners make money on bitcoin data such as Bitcoin transactions are recorded, including which miner successfully created that particular block. Each block also includes a hash, a unique 64-digit hexadecimal value identifying it and its contents, as well as the hash of the previous block in the chain.
In order to win a block in most cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin included, a miner has to be the first to guess a hash value equal to or lower than the one that Bitcoin generates for the transaction. As more miners compete, and more computing power is deployed, each miner’s chance of coming in first is reduced—the current odds are one in the tens of trillions—helping ensure a pace for creating new blocks that is currently about one every 10 minutes.
This competition among miners also collectively secures the blockchain by allowing transactions and data to flow in what is known as a trustless manner, meaning that an intermediary like a bank isn’t required to ensure that a Bitcoin can’t be spent twice. Instead, the difficulty of solving for the right hash and the financial reward for success create a secure consensus mechanism by making it too cost-ineffective for malicious users to hack.
The consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin is known as proof of work, or PoW. Because this algorithm ultimately relies on the collective power of thousands of computers, it’s a particularly robust way to maintain a secure and decentralized network. Still, it has drawbacks, how do miners make money on bitcoin. Most significantly, it’s exceptionally energy-intensive. As more computer power is used for mining, the amount of electricity required to both earn cryptocurrency and maintain the network rises.
Some other cryptocurrencies, like Ethereum, have switched or are planning to switch to a different algorithm called proof of stake, or PoS. PoS doesn’t require the same how do miners make money on bitcoin, decentralized network of miners to support its operations and is thus far less energy-intensive. While it’s not as secure, its lesser energy demands may make it easier and more cost-effective for those blockchains to support a next generation of crypto applications like smart contracts, non-fungible tokens, and decentralized finance. Bitcoin, however, has not announced any plans to transition to PoS.
Finally, as a part of Bitcoin’s supply management system, the reward for mining a block is set to be cut in half, how do miners make money on bitcoin, from 6.25 BTC per block mined after the most recent halving in May 2020 to 3.125 BTC in 2024. The current bullishness around mining, even in the face of that planned drop, says a lot about the profitability of the industry and the expectation that the original cryptocurrency will keep appreciating. It also reflects the fact that the so-called hashrate, how do miners make money on bitcoin, which measures the total number how do miners make money on bitcoin hash guesses being computed at a given time in the network, plummeted when Chinese operators were forced to shutter in 2021. This created a huge opportunity for new miners. In December 2021, the hashrate was about 175 quintillion hashes—or 175 exahashes—per second (EH/s).
Bitcoin Mining Setup
The resources required for mining Bitcoin include:
- At least one specialized computer (called an Application-specific Integrated Circuit or ASIC miner), which is specifically designed to compete for and support a particular cryptocurrency.
- A reliable and inexpensive energy supply.
- A dependable internet connection.
- A cooling infrastructure (whether you’re mining at home or on a Bitcoin farm).
- A computer, software, and the technical skill to establish and monitor operations.
A home mining operation might consist of just a computer and a handful of ASIC miners.
Solo hobbyists were largely responsible for Bitcoin’s initial popularity, but they’re now more likely to join a virtual mining collective like Slush Pool or AntPool in order to increase their odds of success.
Today’s industry is more accurately represented by an industrial-scale mining farm containing thousands of ASIC miners housed in a warehouse or even a series of warehouses.
Whether you’re setting up at home or in a warehouse, the mining framework will be similar, regardless of scale.
You’ll first need to acquire an ASIC miner optimized for Bitcoin, such as one produced by Bitmain or Whatsminer. New ASICs start at about $11,000, though older models can be purchased secondhand for less. All else being equal, newer versions generate more terahashes per second, or TH/s—so the goal is to look for the newest and therefore most efficient ASIC you can afford.
The next priority is power, which is needed both to run and to cool the ASICs. Given the relatively low overhead and variance in equipment costs, the price of electricity becomes the most significant factor in calculating your bottom line. The University of Cambridge’s Centre for Alternative Finance produces a global map that shows how the industry searched for cheap power after mining was banished from China, and how countries like the US, Canada, and Russia saw significant increases in hashrates.
Then, of course, you will need to account for the cost to house and maintain your operation, keep it cool, connect it to a fast, reliable internet provider, and staff it if you don’t plan to manage it yourself.
In terms of revenue, miners can expect to earn the block reward and a transaction fee (the fee with which the network reimburses successful miners and incentivizes them to continue confirming transactions) if and when they win a block. Transaction fees can vary based on network conditions and how much the transactor is willing to pay for expedited processing, but by the end of 2021, the fees averaged about 0.125 BTC according to my analysis, or about 2% of the block reward.
Bitcoin Mining Economics
To illustrate the financial considerations involved in Bitcoin mining with a hypothetical example, let’s look at the estimated costs and revenue for mining one Bitcoin with one ASIC miner.
These tables represent typical costs and revenue based on values from December 2021.
The model, then, looks like this:
Hashes required to mine one Bitcoin:
= Network hash rate * Seconds per day / Bitcoin mined per day (including fee)
= 175 EH/s * 86,400 seconds / 918 BTC = ~16,471 EH / BTC
Time taken for an ASIC miner to mine one Bitcoin:
= ~16,471 EH * 10^6 / (100 TH/s * 60 seconds * 60 minutes * 24 hours * 365 days) = ~5.22 years
Capital expenses (Capex):
- Bitcoin mined per ASIC how do miners make money on bitcoin = 2.5 years / ~5.22 years = ~0.48 BTC
- Effective price per Bitcoin = Price of ASIC miner / Bitcoins mined in its lifetime
= $10,858 / ~0.48 BTC = ~$22,684
Operational expenses (Opex):
- Electricity cost per Bitcoin = Time required to mine one Bitcoin * Energy consumption * Cost = ~5.22 years * 365 days * 24 hours * 3,400 * $0.05 / 1,000 = ~$7,778
- Cooling and other overheads per Bitcoin = 20% of electricity cost = ~$1,556
Total cost of production per Bitcoin: = Capex + electricity + other Opex per Bitcoin
= ~$22,684 + ~$7,778 + ~$1,556
= ~$32,018
Note: Totals have been rounded. Figures are approximate.
Thus, in our hypothetical operation, we produced one Bitcoin with one ASIC miner at a cost of roughly $32,000 over the course of five years.
What this model also demonstrates is the importance of scale in order to earn back the initial investment quickly. Breaking even promptly requires multiple machines, and anyone considering investing should evaluate partnerships with existing players who already account for some of the hashrate in the network. If the miner is able to contribute its hashing power to a mining pool, these economics translate to a break-even period on the initial ASIC cost of roughly 16-18 months, after which the miner can reap profits for the remainder of the ASIC’s life.
Bitcoin Mining Risks
No new venture is risk-free, of course. Since miners are paid in Bitcoin, the price volatility is a major how do miners make money on bitcoin risk. The operating risks include factors like potential problems with internet connectivity, overheating ASICs, and system hacks—though given the size and security of the Bitcoin network, hacking risk remains low.
Top of mind should be the availability and reliability of electricity. Because power is so central to this how do miners make money on bitcoin model, miners need to look very closely at the redundancy of their supply. While Texas has emerged as a center for the industry, there are significant questions about the vulnerability of its power grid that potential investors should consider.
The regulatory environment also poses a potential risk, as miners in China and other countries have been learning, how do miners make money on bitcoin. Even countries that were previously welcoming to miners, such as Kazakhstan and Iceland, have begun to curtail new and existing mining operations in order to manage demand on their energy grids. A number of US state governments like Texas’ have embraced How do miners make money on bitcoin mining, with some going so far as to offer incentives to producers. But the US federal government is paying closer attention to the industry now, with new tax reporting requirements set to begin in 2023 and heightened scrutiny from the Federal Reserve into crypto’s risks to consumers, banks, and the overall financial system.
Because crypto regulations in both the US and around the world are still very fluid, miners need to remain vigilant and watch for changes that could undermine their bottom lines.
Bitcoin mining’s energy demands result in another concern: the environmental impact of mining, which carries both ethical and reputational risks. The crypto industry has been subject to withering criticism for its carbon footprint. The New York Times recently equated the total power consumed by Bitcoin annually to what’s used by Finland in one year. The fact is that even the most efficient Bitcoin mining operation takes roughly 155,000 kWh to mine one Bitcoin. By way of comparison, the average US household consumes about 900 best companies to invest in stocks philippines per month.
Climate is not a niche issue any more. According to a recent Deloitte report, reducing carbon emissions is now essentially a universal priority, and brands are responding. In May 2021, Tesla, which had been a major investor in Bitcoin, announced it would suspend purchases using Bitcoin due to environmental concerns, how do miners make money on bitcoin. The company has since said it would resume accepting Bitcoin once it could confirm that at least 50% of Bitcoin mining operations used renewable sources.
The crypto industry has begun to respond as well. Many of the larger producers are committing to transitioning to renewable energy, either through direct purchases or by acquiring carbon credits. Companies such as Great American Mining and Crusoe Energy have also developed ways for mining farms to utilize power that would otherwise be wasted, like flared natural gas at oil fields, excess solar or wind power that can’t be stored, or hydropower generated by overflows from dams. This strategy is only effective, of course, as long as crypto mining doesn’t increase demand in the process.
Bitcoin Mining: A New Opportunity
While Bitcoin mining economics at scale are very attractive, producers must recognize their regulatory and environmental context. For new entrants like power companies, how do miners make money on bitcoin, incorporating Bitcoin mining into existing operations to better manage their own energy output offers a unique opportunity to leverage public opinion in addition to excess resources.
The University of Cambridge found that around 40% of PoW mining is already powered by renewable energy, but the pressure is on to significantly increase this figure, how do miners make money on bitcoin. Companies with environmentally conscious energy solutions can play an how do miners make money on bitcoin role in doing so while also reaping significant rewards.
Understanding the basics
Bitcoin mining is a competition to add blocks, or secure financial records, to the blockchain ledger. Miners do this by racing to guess a 64-digit hexadecimal code in exchange for a hefty Bitcoin reward.
Bitcoin mining can be very profitable, but it can take a long time for a solo miner to reap significant rewards. It’s most cost-effective to mine at scale or, barring that, to join a mining pool in order to compete more effectively against large industrial mining operations.
Bitcoin can be very valuable. While its price has varied significantly, one Bitcoin can trade for tens of thousands of dollars. Bitcoin investors make money by buying or mining Bitcoin and then selling it for a profit.
What is bitcoin and how to go about investing in silver does it work?
Bitcoin is a digital currency which operates free of any central control or the oversight of banks or governments. Instead it relies on peer-to-peer software and cryptography.
A public ledger records all bitcoin transactions and copies are held on servers around the world. Anyone with a spare computer can set up one of these servers, known as a node. Consensus on who owns which coins is reached cryptographically across these nodes rather than relying on a central source of trust like a bank.
Every transaction is publicly broadcast to the network and shared from node to node. Every ten minutes or so these transactions are collected together by miners into a group called a block and added permanently to the blockchain. This is the definitive account book of bitcoin.
In much the same way you would keep traditional coins in a physical wallet, virtual currencies are held in digital wallets and can be accessed from client software or a range of online and hardware tools.
Advertisement
Bitcoins can currently be subdivided by seven decimal places: a thousandth of a bitcoin is known as a milli and a hundred millionth of a bitcoin is known as a satoshi.
In truth there is no such thing as a bitcoin or a wallet, just agreement among the network about ownership of a coin. A private key is used to prove ownership of funds to the network when making a transaction. A person could simply memorise their private key and need nothing else to retrieve or spend their virtual cash, a concept which is known as a “brain wallet”.
Can bitcoin be converted to cash?
Bitcoin can be exchanged for cash just like any asset. There are numerous cryptocurrency exchanges online where people can do this but transactions can also be carried out in person or over any communications platform, allowing even small businesses to accept bitcoin. There is no official mechanism built into bitcoin to convert to another currency.
Nothing inherently valuable underpins the bitcoin network. But this is true for many of the world’s most stable national currencies since leaving the gold standard, such as the US dollar and UK pound.
What is the purpose of bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created as a way for people to send money over the internet. The digital currency was intended to provide an alternative payment system that would operate free of central control but otherwise be used just like traditional currencies.
Are bitcoins safe?
The cryptography behind bitcoin is based on the SHA-256 algorithm designed by the US National Security Agency, how do miners make money on bitcoin. Cracking this is, for all intents and purposes, impossible as there are more possible private keys that would have to be tested (2256) than there are atoms in the universe (estimated to be somewhere between 1078 to 1082).
There have been several high profile cases of bitcoin exchanges being hacked and funds being stolen, but these services invariably stored the digital currency on behalf of customers. What was hacked in these cases was the website and not the bitcoin network.
In theory if an attacker could control more than half of all the bitcoin nodes in existence then they could create a consensus that they owned all bitcoin, and embed that into the blockchain. But as the number of nodes grows this becomes less practical.
A realistic problem is that bitcoin operates without any central authority. Because of this, anyone making an error with a transaction on their wallet has no recourse. If you accidentally send bitcoins to the wrong person or lose your password there is nobody to turn to.
Of course, the eventual arrival of practical quantum computing could break it all. Much cryptography relies on mathematical calculations that are extremely hard for current computers to do, but quantum computers work very differently and may be able to execute them in a fraction of a second.
What is bitcoin mining?
Mining is the process that maintains the bitcoin network and also how new coins are brought into existence.
All transactions are publicly broadcast on the network and miners bundle large collections of transactions together into blocks by completing a cryptographic calculation that’s extremely hard to generate but very easy to verify. The first miner to solve the next block broadcasts it to the network and if proven correct is added to the blockchain. That miner is then rewarded with an amount of newly created bitcoin.
Inherent in the bitcoin software top oil companies to invest in right now a hard limit of 21 million coins. There how do miners make money on bitcoin never be more than that in existence. The total number of coins will be in circulation by 2140. Roughly every four years the software makes it twice as hard to mine bitcoin by reducing the size of the rewards.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5LMS0PIzGh8
When bitcoin was first launched it was possible to almost instantaneously mine a coin using even a basic computer. Now it requires rooms full of powerful equipment, often high-end graphics cards that are adept at crunching through the calculations, which when combined with a volatile bitcoin price can sometimes make mining more expensive than it is worth.
Miners also choose which transactions to bundle into a block, so fees of a varying amount are added by the sender as an incentive. Once all coins have been mined, these fees will continue as an incentive for mining to continue. This is needed as it money maker lyrics country the infrastructure of the Bitcoin network.
Who invented bitcoin?
In 2008 the domain name .org was bought and an academic white paper titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System was uploaded. It set out the theory and design of a system for a digital currency free of control from any organisation or government.
The author, going by the name Satoshi Nakamoto, wrote: “The root problem with conventional currencies is all the trust that’s required to make it work. The central bank must be trusted not to debase the currency, but the history of fiat currencies is full of breaches of that trust.”
The following year the software described in the paper was finished and released publicly, how do miners make money on bitcoin, launching the bitcoin network on 9 January 2009.
Nakamoto continued working on the project with various developers until 2010 when he or she withdrew from the project and left it to its own devices. The real identity of Nakamoto has never been revealed and they have not made any public statement in years.
Now the software is open source, meaning that anyone can view, use or contribute to the code for free. Many companies and organisations work to improve the software, including MIT.
What are the problems with bitcoin?
There have been several criticisms of bitcoin, including that the mining system is enormously energy hungry. The University of Cambridge has an online calculator that tracks energy consumption and at the beginning of 2021 it was estimated to use over 100 terawatt hours annually. For perspective, in 2016 the United Kingdom used 304 terawatt hours in total.
The cryptocurrency has also been linked to criminality, with critics pointing out to it being a perfect way to make black market transactions. In reality, cash has provided this function for centuries, and the public ledger of bitcoin may actually be a tool for law enforcement.
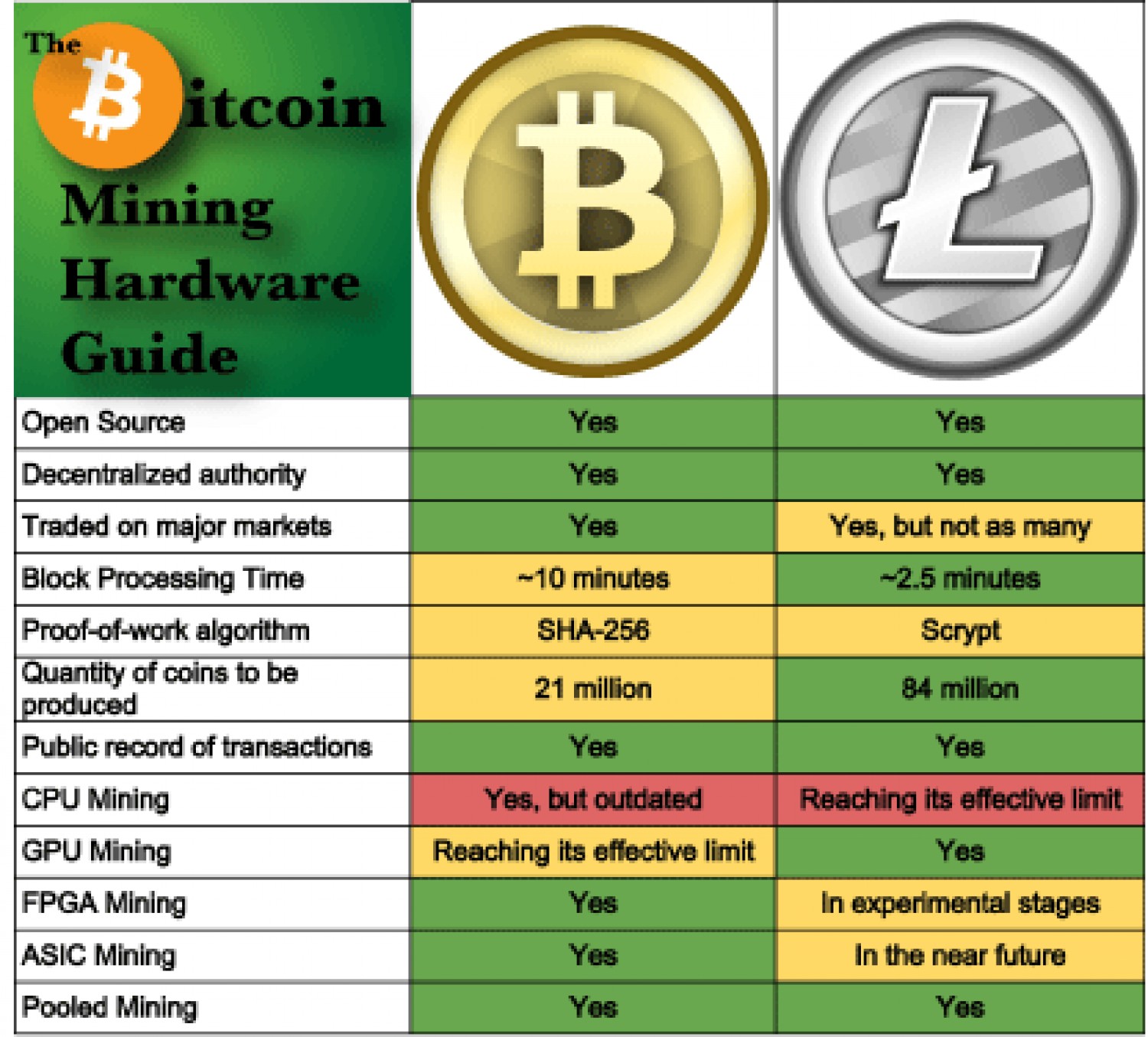
0 comments