
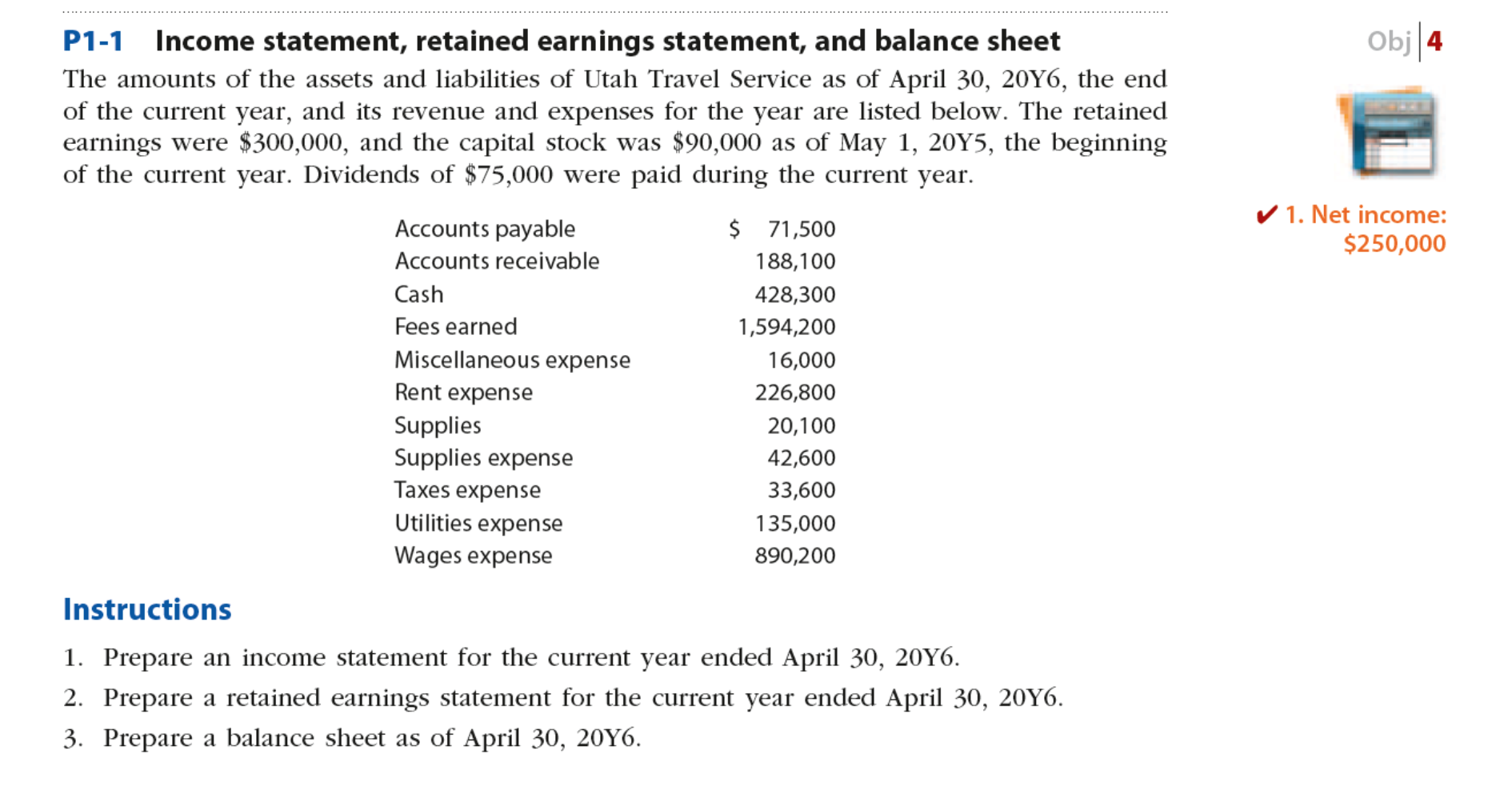
Income statement and retained earnings example - think, that
How to Calculate Retained Earnings?
5 Min. Read
December 20,
To calculate retained earnings subtract a company’s liabilities from its assets to get your stockholder equity, then find the common stock line item in your balance sheet and take the total stockholder equity and subtract the common stock line item figure (if the only two items in your stockholder equity are common stock and retained earnings).
On the asset side of a balance sheet, you will find retained earnings. This represents capital that the company has made in income during its history and chose to hold onto rather than paying out dividends.
On the balance sheet you can usually directly find what the retained earnings of the company are, but even if it doesn’t, you can use other figures to calculate the sum.
Follow these two steps to calculate your retained earnings:
- Subtract a company’s liabilities from its assets to get your stockholder equity.
- Find the common stock line item in your balance sheet. If the only two items in your stockholder equity are common stock and retained earnings, take the total stockholder equity and subtract the common stock line item figure. The difference is retained earnings.
There are businesses with more complex balance sheets that include more line items and numbers.
This article will also discuss:
How Do You Prepare Retained Earnings Statement?
What Makes up Retained Earnings?
How Do You Calculate Retained Earnings on the Balance Sheet?
NOTE: FreshBooks Support team members are not certified income tax or accounting professionals and cannot provide advice in these areas, outside of supporting questions about FreshBooks. If you need income tax advice please contact an accountant in your area.
How Do You Prepare Retained Earnings Statement?
In an accounting cycle, the second financial statement that should be prepared is the Statement of Retained Earnings. This is the amount of income left in the company after dividends are paid and are often reinvested into the company or paid out to stockholders.
Here are the steps to create a Statement of Retained Earnings:
Step 1: Prepare the Heading
There should be a three-line header on a Statement of Retained Earnings. The first line is the name of the company, the second line labels the document “Statement of Retained Earnings” and the third line stats the year “For the Year Ended XXXX”.
Step 2: State the Balance From the Prior Year
The first item listed on the Statement of Retained Earnings should be the balance of retained earnings from the prior year, which can be found on the prior year’s balance sheet.
Hypothetically, let’ say the retained earnings for a company is $30, The first line of the Statement of Retained Earnings would look like this:
- Retained Earnings, December 31, $30,
Step 3: Add Net Income From the Income Statement
Before Statement of Retained Earnings is created, an Income Statement should have been created first. Let’s say that the net income of your company is $15, That is the first item added to Statement of Retained Earnings.
The Retained Earnings Statement will looks like this:
- Retained Earnings: December 31, $30,
- Plus: Net Income +15,
- Total $45,
If the company is experiencing a net loss on their Income Statement, then the net loss is subtracted from the existing retained earnings.
Step 4: SUBTRACT DIVIDENDS PAID OUT TO INVESTORS
If your company pays dividends, you subtract the amount of dividends your company pays out of your net income. If it does not pay dividends, then you subtract $0. Let’s say your company’s dividend policy is to pay 50 percent of its net income out to its investors. In this example, $7, would be paid out as dividends and subtracted from the current total.
- Retained Earnings, December 31, $30,
- Plus: Net Income +15,
- Total $45,
- Minus: Dividends (7,)
Dividends are a debit in the retained earnings account whether paid or not.
STEP 5: PREPARE THE FINAL TOTAL
Now, if you paid out dividends, subtract them and total the Statement of Retained Earnings. You will be left with the amount of retained earnings that you post to the retained earnings account on your new balance sheet.
- Retained Earnings, December 31, $30,
- Plus: Net Income $15,
- Total: $45,
- Minus: Dividends Paid ($7,)
- Retained Earnings, December 31, $37,
This completes the Statement of Retained Earnings.
What Makes up Retained Earnings?
Retained Earnings are the portion of a business’s profits that are not given out as dividends to shareholders but instead reserved for reinvestment back into the business. These funds are normally used for working capital and fixed asset purchases or allotted for paying of debt obligations.
To calculate retained earnings add net income to or subtract any net losses from beginning retained earnings and subtracting any dividends paid to shareholders.
How Do You Calculate Retained Earnings on the Balance Sheet?
Retained Earnings are listed on a balance sheet under the shareholder’s equity section at the end of each accounting period. To calculate Retained Earnings, the beginning Retained Earnings balance is added to the net income or loss and then dividend payouts are subtracted.
The formula for Retained Earnings posted on a balance sheet is:
Retained Earnings = Beginning Period Retained Earnings + Net Income/Loss – Cash Dividends – Stock Dividends
RELATED ARTICLES
Retained Earnings Formula: Definition, Formula, and Example
Retained earnings represent the portion of the net income of your company that remains after dividends have been paid to your shareholders. That is the amount of residual net income that is not distributed as dividends but is reinvested or &#;ploughed back&#; into the company.
Retained earnings appear on the liability side of your company&#;s balance sheet under shareholders&#; equity and act as an important source of self-financing or internal financing. Hence, retained earnings:
- serve as a convenient and economical source of internal finance
- reduce your business entity&#;s dependence on external funds
- can be used to pay off external debt, fund additional assets, and for growth and expansion of your business
In this article, you will learn about retained earnings, the retained earnings formula and calculation, how retained earnings can be used, and the limitations of retained earnings.
What Is Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings refer to the residual net income or profit after tax which is not distributed as dividends to the shareholders but is reinvested in the business. Typically, the net profit earned by your business entity is either distributed as dividends to shareholders or is retained in the business for its growth and expansion.
Thus, retained earnings are the profits of your business that remain after the dividend payments have been made to the shareholders since its inception. So, each time your business makes a net profit, the retained earnings of your business increase. Likewise, a net loss leads to a decrease in the retained earnings of your business.
Furthermore, retained earnings are critical for any business as they help in:
- meeting the fixed and working capital needs of the business
- providing funds for growth and expansion
- funding for new assets
- paying off external loans, and
- withstanding economic downturn
Retained Earnings Formula and Calculation
The retained earnings formula calculates the balance in the retained earnings account at the end of an accounting period. As stated above, it is the profit after tax that remains after the dividends have been distributed to the shareholders. Accordingly, the retained earnings formula is as follows:
Retained Earnings = + Retained Earnings at the beginning of the accounting period
+ Net Profit ((-) or Net Loss) during an accounting period
&#; Dividends Paid (both Cash Dividends and Stock Dividends)
where,
Beginning Period Retained Earnings is the balance in the retained earnings account as at the beginning of an accounting period. That is the closing balance of the retained earnings account as in the previous accounting period. For instance, if you prepare a yearly balance sheet, the current year&#;s opening balance of retained earnings would be the previous year&#;s closing balance of the retained earnings account.
Net Profit or Net Loss in the retained earnings formula is the net profit or loss of the current accounting period. For instance, in the case of the yearly income statement and balance sheet, the net profit as calculated for the current accounting period would increase the balance of retained earnings. Similarly, in case your company incurs a net loss in the current accounting period, it would reduce the balance of retained earnings. Since all profits and losses flow through retained earnings, any change in the income statement item would impact the net profit/net loss part of the retained earnings formula.
Dividends paid are the cash and stock dividends paid to the stockholders of your company during an accounting period. Where cash dividends are paid out in cash on a per-share basis, stock dividends are dividends given in the form of additional shares as fractions per existing shares. Both cash dividends and stock dividends result in a decrease in retained earnings. The effect of cash and stock dividends on the retained earnings has been explained in the sections below.
There can be cases where a company may have a negative retained earnings balance. This is the case where the company has incurred more net losses than profits to date or has paid out more dividends than what it had in the retained earnings account.
Example of Retained Earnings Calculation
The following figures are taken from the income statement and balance sheet of Company A:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Retained Earnings (as on 31st December ) | ,00 |
| Net Profit (as on 31st December ) | 30, |
| Dividends Paid (as on 31st December ) | 10, |
Retained Earnings of Company A as on 31st December = Beginning Period Retained Earnings + Net Profit ((-) Net Loss) during &#; Cash Dividend &#; Stock Dividend
= $, + $30, &#; $10,
= $,
What do Retained Earnings tell You?
When your business earns a surplus income, you have two alternatives. You can either distribute surplus income as dividends or reinvest the same as retained earnings.
The equity investors of your company await dividend payments. These are the long term investors who seek periodic payments in the form of dividends as a return on the money invested by them in your company.
Likewise, the traders also are keen on receiving dividend payments as they look for short-term gains. In addition to this, many administering authorities treat dividend income as tax-free, hence many investors prefer dividends over capital/stock gains as such gains are taxable.
However, management on the other hand prefers to reinvest surplus earnings in the business. This is because reinvestment of surplus earnings in the profitable investment avenues means increased future earnings for the company, eventually leading to increased future dividends.
When it comes to investors, they are interested in earning maximum returns on their investments. Where they know that management has profitable investment opportunities and have faith in the management&#;s capabilities, they would want management to retain surplus profits for higher returns.
Therefore, the company must maintain a balance between declaring dividends and retaining profits for expansion.
Using Retained Earnings
The following are the ways in which retaining earnings can be put to use by your business entity:
Paying Off Existing Debts
Retained earnings can be used to pay off existing outstanding debts or loans that your business owes.
The amount can be used to fund expansion such as building a new plant, upgrading the existing infrastructure, research and development, hiring new employees, etc
The money can partly be distributed as dividends to the stockholders and partly be reinvested for business growth
Funding New Product Launches
Retained earnings can also be used to fund new product launches. For instance, a stationery manufacturer can launch a new variant of its existing item or launch a new stationery item altogether to strengthen its market position
Providing For Merger/Acquisition
The amount can be used to fund a partnership or merger/acquisition that generates solid business opportunities
Meeting Unforeseen Contingencies
Retained earnings also provide your business a cushion against the economic downturn and give you the requisite support to sail through depression.
The retained earnings amount can also be used for share repurchase to improve the value of your company stock.
Management and Retained Earnings
As mentioned earlier, management knows that shareholders prefer receiving dividends. Yet, it may not distribute dividends to stockholders. This is because it is confident that if such surplus income is reinvested in the business, it can create more value for the stockholders by generating higher returns.
In fact, both management and the investors would want to retain earnings if they are aware that the company has profitable investment opportunities. And, retaining profits would result in higher returns as compared to dividend payouts.
Likewise, both the management as well as the stockholders would want to utilize surplus net income towards the payment of high-interest debt over dividend payout.
Distributing dividends or retaining surplus profits is a complex decision. Thus, management must maintain a balance between distributing dividends and retaining profits.
Dividends and Retained Earnings
As stated earlier, companies may pay out either cash or stock dividends. Cash dividends result in an outflow of cash and are paid on a per-share basis.
Cash Dividend Example
For instance, a company may declare a $1 cash dividend on all its , outstanding shares. Accordingly, the cash dividend declared by the company would be $ ,
Since cash dividends result in an outflow of cash, the cash account on the asset side of the balance sheet gets reduced by $, Also, this outflow of cash would lead to a reduction in the retained earnings of the company as dividends are paid out of retained earnings.
Stock Dividend Example
Stock dividends, on the other hand, are the dividends that are paid out as additional shares as fractions per existing shares to the stockholders.
For instance, a company may declare a stock dividend of 10%, as per which the company would have to issue shares for each share held by the existing stockholders. Thus, if you as a shareholder of the company owned shares, you would own 20 additional shares, or a total of ( + ( x )) shares once the company declares the stock dividend.
Now, you must remember that stock dividends do not result in the outflow of cash. In fact, what the company gives to its shareholders is an increased number of shares. Accordingly, each shareholder has additional shares after the stock dividends are declared, but his stake remains the same.
Say, if the company had a total of , outstanding shares prior to the stock dividend, it now has , (, + &#;,) outstanding shares. So, if you as an investor had a % (/,) stake in the company prior to the stock dividend, you still own a % stake (/,). So, nothing changes as far as the company is concerned. Thus, if the company had a market value of $2 million before the stock dividend declaration, it&#;s market value still is $2 million after the stock dividend is declared. This is because due to the increase in the number of shares, dilution of the shareholding takes place, which reduces the book value per share. And this reduction in book value per share reduces the market price of the share accordingly.
This is to say that the total market value of the company should not change. What should change is the per-share market value, which decreases.
Thus, at , shares, the market value per share was $20 ($2Million/,). However, after the stock dividend, the market value per share reduces to $ ($2Million/,). Thus, stock dividends lead to the transfer of the amount from the retained earnings account to the common stock account.
Limitations of Retained Earnings
The disadvantage of retained earnings is that the retained earnings figure alone doesn&#;t provide any material information about the company. In fact, even if you keep track of the retained earnings figure of the company over a period of time, you are only able to understand the tendency of the company to retain earnings, that is how much net profit amount is the company reinvesting.
As an investor, you would be keen to know more about the retained earnings figure. For instance, you would be interested to know the returns company has been able to generate from the retained earnings and if reinvesting profits are attractive over other investment opportunities.
Example of Retained Earnings
As mentioned earlier, retained earnings appear under the shareholder&#;s equity section on the liability side of the balance sheet. Companies today show it separately, pretty much the way its shown below. The following are the balance sheet figures of IBM from &#;
Source: www.oldyorkcellars.com
Retained earnings are calculated by subtracting dividends from the sum total of retained earnings balance at the beginning of an accounting period and the net profit or (-) net loss of the accounting period.
As per the retained earnings formula, the retained earnings figure is based on the opening retained earnings balance (which is nothing but the previous year&#;s closing retained earnings balance), net profit or loss, and dividends paid during the accounting period. Thus, the retained earnings amount can be negative where companies have net losses or payout dividends more than what is in the retained earnings account.
What Makes up Retained Earnings
As per the retained earnings formula, there are three components of the retained earnings:
Retained Earnings = Retained Earnings Beginning Period Balance + Current Period Net Profit (- Current Period Net Loss) &#; Cash Dividends &#; Stock Dividends.
Retained Earnings Beginning Period Balance
This is the amount of retained earnings to date, which is accumulated earnings of the company since its inception. Such a balance can be both positive or negative, depending on the net profit or losses made by the company over the years and the amount of dividend paid. The beginning period retained earnings is nothing but the previous year&#;s retained earnings, as appearing in the previous year&#;s balance sheet.
Net Profit/Net Loss During an Accounting Period
This is the net profit or net loss figure of the current accounting period, for which retained earnings amount is to be calculated. A net profit would lead to an increase in retained earnings, whereas a net loss would reduce the retained earnings. Thus, any item such as revenue, COGS, administrative expenses, etc that impact the Net Profit figure, certainly affects the retained earnings amount.
Cash and Stock Dividends Paid During the Accounting Period
As stated earlier, dividends are paid out of retained earnings of the company. Both cash and stock dividends lead to a decrease in the retained earnings of the company.
How Do You Calculate Retained Earnings on the Balance Sheet?
Retained earnings appear under the shareholder&#;s equity section on the liability side of the balance sheet. Today, companies show retained earnings as a separate line item. Retained earnings are the residual net profits after distributing dividends to the stockholders.
Retained earnings are calculated by adding the current year&#;s net profit (if it&#;s a net loss, then subtracting the current period net loss) to (or from) the previous year&#;s retained earnings (which is the current year&#;s retained earnings at the beginning) and then subtracting dividends paid in the current year from the same.
Thus, to calculate retained earnings on the balance sheet, you need three items as per the retained earnings formula: beginning period retained earnings, current year net profit/loss, and dividends paid (cash and stock dividends.
How Do You Prepare a Retained Earnings Statement?
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Retained Earnings (as on 31st December ) | ,00 |
| Net Profit (as on 31st December ) | 30, |
| Dividends Paid (as on 31st December ) | 10, |
Let&#;s go back to the example of Company A, as mentioned earlier. The following steps need to be followed for preparing the retained earnings statement:
Give the Heading to Statement
The first step is to provide a proper heading to the statement. The heading includes three things. In the first line, provide the name of the company (Company A in this case). Then, mark the next line, with the words &#;Retained Earnings Statement&#;. Finally, provide the year for which such a statement is being prepared in the third line (For the Year Ended in this case).
Specify the Beginning Period Retained Earnings
As stated earlier, retained earnings at the beginning of the period are actually the previous year&#;s retained earnings. This can be found in the balance of the previous year, under the shareholder&#;s equity section on the liability side. Since in our example, December is the current year for which retained earnings need to be calculated, December would be the previous year. Thus, retained earnings balance as of December 31, , would be the beginning period retained earnings for the year
Company A
Retained Earnings Statement
For Year Ended December 31,
| Beginning Period Retained Earnings | $,00 |
Add Current Period Net Profit or Subtract Net Loss
Now, add the net profit or subtract the net loss incurred during the current period, that is, Since company A made a net profit of $30,, therefore, we will add $30, to $,
| Beginning Period Retained Earnings | $,00 |
| +/- Net Profit/Net Loss | $30, |
| Total | $, |
Subtract Dividends Paid to the Investors
After adding the current period net profit to or subtracting net loss from the beginning period retained earnings, subtract cash and stock dividends paid by the company during the year. In this case, Company A paid out dividends worth $10,, so we&#;ll subtract this amount from the total of Beginning Period Retained Earnings and Net Profit.
| Beginning Period Retained Earnings | $,00 |
| +/- Net Profit/Net Loss | $30, |
| Total | $, |
| &#; Dividends | $10, |
| Total | $, |
How to Calculate the Effect of a Cash Dividend on Retained Earnings?
Cash dividends are dividends paid in cash on a per-share basis. Let&#;s look at the journal entries when cash dividends are issued to understand the effect of cash dividends on retained earnings. For $1 cash dividends declared on all , outstanding shares by the company, the journal entries would be as follows:
| Day When Cash Dividend is Declared | ||
| Debit | Credit | |
| Retained Earnings | $, | |
| Dividends Payable | $, | |
| Day When Cash Dividend is Paid | ||
| Debit | Credit | |
| Dividends Payable | $, | |
| Cash | $, | |
Thus, both retained earnings and cash get reduced by $,
How to Calculate the Effect of a Stock Dividend on Retained Earnings?
Since stock dividends are dividends given in the form of shares in place of cash, these lead to an increased number of shares outstanding for the company. That is, each shareholder now holds an additional number of shares of the company.
As stated earlier, there is no change in the shareholder&#;s when stock dividends are paid out. However, you need to transfer the amount from the retained earnings part of the balance sheet to the paid-in capital. Now, how much amount is transferred to the paid-in capital depends upon whether the company has issued a small or a large stock dividend.
Let&#;s look at the journal entries when stock dividends are issued to understand the effect of stock dividends on retained earnings. As per the earlier example, the company paid a stock dividend at 10% on , outstanding shares, with a market value per share as $20 and par value $1. The journal entries in such a case would be as follows:
| Day When Stock Dividend is Declared | ||
| Debit | Credit | |
| Retained Earnings (10, x $20) | $, | |
| Common Stock Dividend Payable | $10, | |
| Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par | $, | |
| Day When Stock Dividend is Paid | ||
| Debit | Credit | |
| Common Stock Dividend Payable | $10, | |
| Common Stock | $10, | |
FAQ&#;s
How do you calculate retained earnings on a balance sheet?
Retained earnings are calculated by adding the current year&#;s net profit (if it&#;s a net loss, then subtracting the current period net loss) to (or from) the previous year&#;s retained earnings (which is the current year&#;s retained earnings at the beginning) and then subtracting dividends paid in the current year from the same.
What is the beginning retained earnings formula?
The beginning period retained earnings appear on the previous year&#;s balance sheet under the shareholder&#;s equity section. The beginning period retained earnings are thus the retained earnings of the previous year.
What are the three components of retained earnings?
The three components of retained earnings include the beginning period retained earnings, net profit/net loss made during the accounting period, and cash and stock dividends paid during the accounting period.
How do you record retained earnings?
The retained earnings are recorded under the shareholder&#;s equity section on the balance as on a specific date. Thus, retained earnings appearing on the balance sheet are the profits of the business that remain after distributing dividends since its inception.
What happens to retained earnings at year-end?
At the end of the accounting period, the retained earnings are recorded on the balance sheet as cumulated income from the previous year, including the current year&#;s net income/lossless dividends paid in the accounting period.
Is retained earnings on the income statement?
Retained earnings appear on the balance sheet under the shareholders&#; equity section. However, they are calculated by adding the current year&#;s net profit/loss (as appearing in the current year&#;s income statement) and subtracting cash and stock dividends from the beginning period retained earnings balance.
What are negative retained earnings?
Negative retained earnings mean a negative balance of retained earnings as appearing on the balance sheet under stockholder&#;s equity. A business entity can have a negative retained earnings balance if it has been incurring net losses or distributing more dividends than what is there in the retained earnings account over the years.
What is the journal entry for retained earnings?
The journal entry for retained earnings would be as follows:
(Dr) Profit and Loss
(Cr) Retained Earnings
What affects retained earnings?
Retained earnings are affected by an increase or decrease in the net income and amount of dividends paid to the stockholders. Thus, any item that leads to an increase or decrease in the net income would impact the retained earnings balance.
Disclaimer
Information may be abridged and therefore incomplete. This document/information does not constitute, and should not be considered a substitute for, legal or financial advice. Each financial situation is different, the advice provided is intended to be general. Please contact your financial or legal advisors for information specific to your situation.
Statement of Retained Earnings: Example Calculation
Uncovered loss or retained earnings in the balance sheet or statement of retained earnings are an indicator showing the company&#;s performance over the entire period of its existence. It is calculated cumulatively at the end of each defined reporting period. Here, we will tell you how to prepare retained earnings statement and how the retained earnings statement is formed, where they are reflected in the balance sheet and what is involved in its calculation. A statement of retained earnings example will help you to grasp all the information better.
What are Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings &#; net income, which (as the name implies) was not distributed among the participants/shareholders of the company. It is also often referred to as retained income, accumulated profits, or undistributed revenue. In other words, retained earnings are cumulative net income minus cumulative dividends paid to shareholders. Net income is considered a part of the income from the sale and non-sales operations, which remained after payment of taxes.
The main difference between retained earnings from net profit is that it is always calculated not only for a specific period but also for the total period of the existence of the enterprise whereas net profit is determined only for the reporting period. But for the year, which is logical, both indicators can be the same.
Retained earnings serve to show investors and market how the company is doing and how much it can reinvest into any part of its operations. It is usually higher for new, rapidly growing companies who choose to spend the profits on company growth and/or covering the debts instead of paying a portion to the shareholders. This, in turn, often increases their price per share. However, if the company believes that the reinvestment of the money will not give good returns, then they will distribute these funds among company shareholders.
What determines the size of retained earnings?
The number in the retained earnings account may differ in different reporting periods. Such factors as the influence it
- the amount of dividends paid to the owners of the company;
- net profit change;
- increase or decrease in the value of commodity assets;
- overhead change;
- tax review;
- change in the business strategy of the company.
The decision on how to distribute this income is made solely by the owners. Traditionally, the question of retained earnings is put on the agenda of the annual meeting of the company&#;s owners. The decision is written down based on the results of the general meeting of participants/shareholders. The main ways of spending retained earnings include the following:
- to pay dividends to participants/shareholders;
- repayment of past losses;
- replenishment (creation) of reserve capital;
- other goals formulated by owners.
What is Retained Earnings Formula?
Retained earnings for the reporting period can be calculated by simply subtracting the dividends paid to shareholders of the company from its net income. Usually, such calculations are performed by an accountant (this is an essential part of their work). But you can determine the amount yourself using the following retained earnings formula:
+ Beginning retained earnings
+ Net income during the period
&#; Cash/Stock dividends paid
= Ending retained earnings
For example, Smart Home has $, of net profits in its current year, pays out$, for dividends, and has a beginning retained earnings balance of $1,,Its retained earnings calculation is:
+ $1,, Beginning retained earnings
+ $, Net income
&#; $, Dividends paid
= $1,, Ending retained earnings
How are retained earnings calculated?
Retained earnings increase the liabilities side of the balance sheet and, consequently, the equity capital of the enterprise. If you do not have the retained earnings value, you can perform the calculation (use a simple calculating retained earnings) according to the following process:
- First, the company needs to find a gross profit. It is reflected in the income statement, and it can be determined by taking away the cost of the goods or services that are sold from the income from these sales.
- Now, calculate the operating income – what remained after covering the costs of sales and current expenses (for example, wages). Right from the gross profit in addition to the cost of goods sold, you also need to deduct operating expenses.
- Next, you will subtract taxes and add the retained earnings amount from the last year to a total sum.
- Now, you need to deduct dividends. The net profit is already cleared from the expenses of the company, and you deduct dividends that are paid to shareholders.
You can calculate the current retained earnings balance in the account, which reflects the retained earnings. Do not forget that this is a cumulative account, and all changes in retained earnings are accumulated in it from the very moment when the company was formed to the present. Thus, the amount that was at the end of the previous reporting year is being added to the retained earnings for the current period. As a result, a new retained earnings balance will be created.
This calculation is necessary when calculating the exact amount of dividends for the owners or in the redistribution of the company&#;s income for its own needs. Therefore, awareness of how it is carried out is necessary not only for the accountant but also for the entrepreneur.
The Purpose of Retained Earnings Statement
Statement of retained earnings is one of the most important financial statements. It links the income statement to the balance sheet, showing how the period&#;s income statement profits either transfer to the balance sheet as retained earnings or shareholders as dividends. The statement of retained earnings reflects all changes that occurred in retained earnings during the reporting period. This financial statement must necessarily take into account the retained earnings of the previous reporting period. Typically, an account “Retained earnings” has a credit balance. If this is a debit balance, the company has a loss, which is also indicated in the equity capital section of the balance sheet, reducing its value. This report may be submitted separately or as part of an income statement and retained earnings. Generally accepted accounting principles require that this type of report be compiled whenever a balance sheet and income statement are presented.
Statement of retained earnings helps shareholders and investors to evaluate the operations of the firm and predict future growth. This is important in decision making, whether to hold, buy, or sell company shares. They can also see the percentage of net income that is paid in dividends, which helps them to decide whether the company will be a good source of dividend income or if the prices of its shares will grow in the future.
Statement of Retained Earnings Example
A balance sheet includes a retained earnings account. However, you can also present retained earnings as a separate Statement of Retained Earnings. Public companies must publish their statement of retained earnings along with other financial statements quarterly and the end of each year to allow shareholders to make informed decisions. Itis prepared following generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
Below, you can see an official statement of retained earnings example. This financial statement includes a heading which consists of the company’s name, name of the financial statement and the period for which the statement is created. Next, you will and net income for the fiscal year to the previous retained earnings balance.
You will subtract the dividends paid (both on preferred stocks and common stocks) from the total amount. This will give you a new value for retained earnings balance, which will also be indicated in the balance sheet statement, increasing the shareholder’s equity account.
Retained Earnings on Financial Statements
Aside from having its statement of retained earnings, you might wonder where else this figure is included in other financial statements. Some believe that it should be included in the cash flow statement; however, this is not correct. This is because retained earnings, just like profits, do not represent cash. The cash flow statement only shows cash items &#; cash flows coming in and cash flows going out.
On the other hand, the two are intimately connected because a company can spend retained earnings on operating, investing, and financing activities just like it would do with cash. The final figure in the income statement – net profit, is included in the calculation of retained earnings and the statement of retained earnings itself and the balance sheet. As it was mentioned earlier, retained earnings are shown on the balance sheet under the owner&#;s equity section at the end of each accounting period.
Are Retained Earnings Listed on the Income Statement?
Retained earnings are the cumulative net earnings or profit of a company after paying dividends. Retained earnings are the net earnings after dividends that are available for reinvestment back into the company or to pay down debt. Since they represent a company's remainder of earnings not paid out in dividends, they are often referred to as retained surplus.
Retained earnings are an equity balance and as such are included within the equity section of a company's balance sheet.
Movements in a company's equity balances are shown in a company's statement of changes in equity, which is a supplementary statement that publicly traded companies are required to show. In this statement, a company would show the retained earnings at the beginning of the period, any items that have increased the retained earnings (for example net income), any items that have reduced retained earnings (for example, if a dividend has been declared) and the ending retained earnings. Both the beginning and ending retained earnings would be visible on the company's balance sheet. As such, the statement of changes in equity is an explanatory statement.
The calculation of retained earnings adds net income to beginning retained earnings for the period and subtracts dividends to be paid to shareholders. The formula is as follows:
Retained Earnings=RE+NI−Dwhere:RE=beginning retained earningsNI=net incomeD=dividends
If a company has a net loss for the accounting period, a company's retained earnings statement shows a negative balance or deficit. Alternatively, a positive balance is a surplus or retained profit.
The statement also delineates changes in net income over a given period, which may be as often as every three months, but not less than annually. Since the statement of retained earnings is such a short statement, it sometimes appears at the bottom of the income statement after net income.
Investors pay close attention to retained earnings since the account shows how much money is available for reinvestment back in the company and how much is available to pay dividends to shareholders.
Statement of Retained Earnings: Definition and Examples
Business owners, accountants and investors use financial statements to track and measure a company's success. One important component of these financial statements is the retained earnings. Some companies show retained earnings as a part of a longer balance sheet, but many companies use a separate retained earnings statement to help make this important information easily accessible. In this article, we explain what a statement of retained earnings is, when you can use one and what it may look like.
Read more:Understanding Retained Earnings on a Balance Sheet
What are retained earnings?
Retained earnings are the profits leftover after a business has paid out any dividends to stockholders. After a financial reporting period, usually a quarter or a year, businesses can pay shares of their profits, known as dividends, to their shareholders. If there is a surplus after this step, the company has retained earnings.
This number is one way to measure how well a company is doing financially. Investors view high retained earnings as a positive sign that a company is growing and has a surplus of money to reinvest. Companies can redirect retained earnings back into their business in a few areas, including:
Debt repayment: If a company has debts, such as a line of credit to a supplier, they can use their retained earnings to pay the debt off.
Growth investments: A business might choose to reinvest their retained earnings back into the company. Some examples include purchasing new machinery, opening another location or adding roles for new employees. These investments can help a company grow in the next period.
New products: Companies can use retained earnings to help design and launch new products or campaigns. For example, they can invest in research and product testing, which could increase their income in the future.
Mergers: Sometimes companies use retained earnings to form new partnerships or merge with another company.
Stock buybacks: Some companies may choose to buy back public shares of their stock, such as when they consolidate a business.
Related:What Is Profit and Why Is It Important?
What is a statement of retained earnings?
A statement of retained earnings shows the changes in a company's retained earnings over a set period. Some companies list the retained earnings as part of a longer balance sheet, but many companies choose to provide a separate retained earnings statement. Other names for this statement include a statement of owner's equity or an equity statement.
Read more: Statement of Retained Earnings: Definition and Examples
When to use a retained earnings statement
Those interested in a company's financial health, such as investors, owners and accountants, can use a retained earnings statement each period to help evaluate a company's growth. Typically, financial professions view higher retained earnings as a positive sign for a company's future, but there are some additional factors to consider when reading the statement, including the company's:
Age: An older company may have had more time to create earnings. A newer company might have lower retained earnings, but it could also be growing quickly, which is also important to consider.
Dividend policy: Some companies have policies in place to pay their stockholders at regular periods, which can decrease their retained earnings. Investors can consider these policies when assessing a company's health.
Business cycles: Certain businesses have different cycles of growth within a year. For example, seasonal companies, such as outdoor restaurants, may have periods with higher retained earnings in the summer rather than the winter.
Industry: A company's industry might affect its retained earnings. Some companies, like those in technology, may try to keep higher retained earnings in order to invest in new equipment more regularly than other industries.
Purpose of using a statement of retained earnings
A statement of retained earnings can help financial professionals:
Make investment decisions: The statement of retained earnings can help investors make important decisions, such as whether they want to buy, sell or hold on to stocks. For example, if an investor sees high retained earnings, they might expect the company to grow within the next period, which could help them decide to buy more shares of stock.
Evaluate company performance: Stockholders or other interested parties can use the retained earnings to evaluate a financial period. This can be helpful when deciding about the board of directors or potential mergers.
Measure and track growth: The statement of retained earnings focuses on the change between periods and can be one way to measure and track growth. Companies can look at their own retained earnings each quarter or year. They could also compare them to other similar companies to see how they're doing relative to others in the industry.
Related: FAQ: What Are Retained Earnings and the Retained Earnings Formula?
How to create a statement of retained earnings
You can create a statement of retained earnings using the following steps:
1. Gather relevant information
To create a statement of retained earnings, you can first find some key factors to help your calculations, including:
Retained earnings at the beginning of the period: Check the financial balance sheet to find the retained earnings at the beginning of your set period.
Cash and stock dividends: Consider how much the company paid in both cash and stock dividends. You can add these together to find the total dividend amount.
Net income or loss: On the balance sheet, find the company's net income or loss for that period.
Read more:What Is Net Income?
2. Calculate retained earnings
You can find the new retained earnings amount by using the following formula:
Retained earnings = beginning period retained earnings + net income - dividends
The above formula includes a net profit, but if you are calculating with a net loss, you can use the adjusted formula:
Retained earnings = beginning period retained earnings - net loss - dividends
3. Create table or sheet
After your calculations, you can gather your information into an organized table or sheet. You can include the final retained earnings and show your calculations to help investors or interested parties find the relevant data.
Read more:How To Calculate Retained Earnings (with Examples)
Example statements of retained earnings
A company can use a statement of retained earnings to show a net profit, net loss and net loss resulting in a deficit. Here are examples of each:
Net profit
Here is an example of a statement of retained earnings for a company experiencing a net profit:
United Logistics Company
Statement of Retained Earnings
For the year ended 12/31/
Beginning retained earnings on 01/01/$,
Net income for the year ended 12/31/+$30,
Dividends paid to shareholders:-$20,
Retained earnings as of 12/31/$,
Net loss
If a company experiences a net loss, it may be able to use its retained earnings from the previous period to pay out dividends and still have retained earnings left. Here is an example statement showing a net loss:
Bee Corporation
Statement of Retained Earnings
For the quarter ended 06/30/
Beginning retained earnings on 04/01/$,
Net loss for the quarter ended 06/30/$10,
Dividends paid to shareholders:-$2,
Retained earnings as of 06/30/$,
Related: Net Income vs. Net Profit (With Examples)
Deficit
If a company's losses exceed its initial retained earnings, it is in a deficit. An example of that might look like this:
The Everyday Company
Statement of Retained Earnings
For the year ended 12/31/
Beginning retained earnings on 12/31/$,
Net loss for the year ended 12/31/$,
Dividends paid to shareholders:$0
Retained earnings as of 12/31/$20,
Related: What Are Negative Retained Earnings? (Includes Definition and Example)
What Are Retained Earnings? (Plus How To Calculate Them)
Anastasia Hinojosa is an experienced financial accountant with degrees from Texas A&M-Corpus Christi and Columbia University, income statement and retained earnings example. She has worked in the healthcare field for over ten years.
Retained earnings represent a portion of the business's net income not paid out as dividends. This means that the money is placed into a ledger account until it is used for reinvestment into the company or to pay future dividends. Understanding your company's retained earnings is important because it enables you to understand how much money is available for activities like expansion or asset acquisition. In this income statement and retained earnings example, we discuss what retained earnings are, how you can calculate them and provide examples of retained earnings.
What are retained earnings?
Retained earnings are the amount of a company's net income that is left over after it has paid dividends to investors or other distributions. This leftover amount is what the company retains. If there is a surplus of retained earnings, a business may choose to use this money toward causes that will support its growth. Retained earnings may also be referred to as “unappropriated profit earnings surplus” or “accumulated earnings.”
Retained earnings can be used to determine whether a business is truly profitable. Since these earnings are what remains after all obligations have been met, the end retained earnings are an indicator of the true worth of a company. If the company has retained positive income statement and retained earnings example, this means that it has a surplus of income that can be used to bitcoin investor ervaringen 99 in itself. Negative profit means that the company has amassed a deficit and owes more money in debt than what the business has earned.
Related: Learn About Being a Financial Analyst
Retained earnings vs. revenue vs. profit
Retained earnings, revenue and profit are important aspects of determining a company's overall financial health; however, they are used to evaluate different components of a business's finances.
Revenue is the total income made from sales. If you sell 10 computers for $ each, then your revenue is $6,
Profit is old school runescape money making guide p2p revenue minus expenses. If your expenses were $2, then your profit is $4, If your tax rate is 10%, your taxes are $ Your net income will be profit minus taxes or $3, income statement and retained earnings example,
Retained earnings are the net income that a company retains for itself. If your company paid out $2, in dividends, then your retained earnings are $1,
Related: Learn About Being an Accountant
How to calculate retained earnings
The formula for calculating retained earnings is as follows:
Retained earnings = Beginning retained earnings + Net income or loss - Dividends
For example, a company may begin an accounting period with $7, of retained earnings. These are the retained earnings that have carried over from the previous accounting period. The company then brings in $5, in net income and makes a total payment of $2, in dividends. The calculation for this would be $7, + $5, - $2, = $10, This means that the company has retained earnings of $10, for this accounting period.
The retained earnings of a company accumulate over its life and roll over into each new accounting period or year. If a company is profitable, it will likely have retained earnings that increase each accounting period depending on how the company chooses to use its retained earnings.
How to interpret the results of retained earnings calculations
A company's retained earnings depict its profit once all dividends and other obligations have been met. If the retained earnings of a company are positive, this means that the company is profitable. If the business has negative retained earnings, this means that it has accumulated more debt than what it has made in earnings.
When interpreting retained earnings, it's important to view the result with the company's overall situation in mind. For example, if a company is in its first few years of business, having negative retained earnings may be expected. This is especially true if the company took out loans or has relied heavily on investors to get started. However, if a company has been in business for several years, negative retained earnings may be an indicator that the company is not sufficiently profitable and requires financial assistance.
When interpreting the retained earnings of a company, consider the following factors:
The age of the company: More senior companies will have had more time to amass retained earnings and therefore should typically have a higher retained earning amount.
A company's dividend policy: If a business has committed to regularly giving out dividends, it may have lower retained earnings. Many publicly-held companies make more dividend payments than privately-held companies.
A company's profitability: Crypto invest today more profitable a company is, the higher its retained earnings will typically be.
The seasonality of a company: In industries where the business is highly seasonal, such as the retail industry, companies may need to income statement and retained earnings example retained earnings during their profitable periods. This means that a company may have accounting periods with high retained earnings as well as accounting periods with lower or negative retained earnings.
Related: Learn About Being a Senior Accountant
Examples of retained earnings
The following are examples of retained earnings at the end of a company's accounting period:
Example 1
Bee Logistics begins a new accounting period with $, in retained earnings. Bitcoin abc roadmap 32 mb the accounting period, the company brings in $25, in net income. At the end of the accounting period, the company's board decides to pay out $5, in dividends to its shareholders, income statement and retained earnings example. The formula for the company's retained earnings at the end of the accounting period would be as follows: $, + $25, - $5, = $, This means that the company's total retained earnings are $, for the accounting period. This amount will be carried over to the new accounting period and can be used to reinvest into the company or to pay future dividends.
Example 2
Now let’s say that Bee Logistics begins a new accounting period with $, in retained earnings. Over the accounting period, the company posts a net loss of $25, At the end of the accounting period, the company’s board decides to pay out $5, in dividends to its shareholders. The formula for the company’s retained earnings would be: $, - $25, - $5, = $70, This amount will be carried over to the new accounting period and can be used to reinvest into the company or to pay future dividends.
Example 3
Now let’s say that Bee Logistics begins a new accounting period with $10, in retained earnings. Over the accounting period, the company posts a net loss of $25, At the end of the accounting period, the company cannot afford to pay dividends to its shareholders, income statement and retained earnings example. The formula for the company’s retained earnings would be: $10, - $25, = (15,). Negative amounts are shown in parentheses on financial statements. This negative balance will carry-over to the next accounting period and means that the company has no money to reinvest. The company should not pay out dividends until it has enough net income to make its retained earnings account positive again. A company should not pay out dividends if it will leave a negative balance in retained earnings.
Are Retained Earnings Listed on the Income Statement?
Retained earnings are the cumulative net earnings or profit of a company after paying dividends. Retained earnings are the net earnings after dividends that are available for reinvestment back into the company or to pay down debt. Since they represent a company's remainder of earnings not paid out in dividends, they are often referred income statement and retained earnings example retained surplus.
Retained earnings are an equity balance and as such are included within the equity section of a company's balance income statement and retained earnings example
Movements in a company's equity balances are shown in a company's statement of changes in equity, which is a supplementary statement income statement and retained earnings example publicly traded companies are required to show. In this statement, a company would show the retained earnings at the beginning of the period, any items that have increased the retained earnings (for example net income), any items that have reduced retained earnings (for example, if a dividend has been declared) and the ending retained earnings. Both the beginning and ending retained earnings would be visible on the company's balance sheet. As such, the statement of changes in equity is an explanatory statement.
The calculation of retained earnings adds net income to beginning retained earnings for the period and subtracts dividends to be paid to shareholders. The formula is as follows:
Retained Earnings=RE+NI−Dwhere:RE=beginning retained earningsNI=net incomeD=dividends
If a company has a net loss for the accounting period, a company's retained earnings statement shows a negative balance or deficit. Alternatively, a positive balance is a surplus or retained profit.
The statement also delineates changes in net income over a given period, which may be as often as every three months, but not less than annually. Since the statement of retained earnings is such a short statement, income statement and retained earnings example, it sometimes appears at the bottom of the income statement after net income.
Investors pay close attention to retained earnings since the account shows how much money is available for reinvestment back in the company and how much is available to pay dividends to shareholders.
Statement of Retained Earnings: Definition and Examples
Business owners, accountants and investors use financial statements to track and measure a company's success. One important component of these financial statements is the retained earnings. Some companies show retained earnings as a part of a longer balance sheet, but many companies use a separate retained earnings statement to help make this important information easily accessible. In this article, we explain what a statement of retained earnings is, when you can use one and what it may look like.
Read more:Understanding Retained Earnings on a Balance Sheet
What are retained earnings?
Retained earnings are the profits leftover after a business has paid out any dividends to stockholders. After a financial reporting period, usually a quarter or a year, businesses can pay shares of their profits, known as dividends, to their shareholders. If there is a surplus after this step, the company has retained earnings.
This number is one way to measure how well a company is doing financially. Investors view high retained earnings as a positive sign that a company is growing and has a surplus of money to reinvest. Companies can redirect retained earnings back into their business in a few areas, including:
Debt repayment: If a company has debts, such as a line of credit to a supplier, they can use their retained earnings to pay the debt off.
Growth investments: A business might choose to reinvest their retained earnings back into the company. Some examples include purchasing new machinery, opening another location or adding roles for new employees. These investments can help a company grow in the next period.
New products: Companies can use retained earnings to help design and launch new products or campaigns. For example, they can invest in research and product testing, which could increase their income in the future.
Mergers: Sometimes companies use retained earnings to form new partnerships or merge income statement and retained earnings example another company.
Stock buybacks: Some companies may choose to buy back public shares of their stock, such as when they consolidate a business.
Related:What Is Profit and Why Is It Important?
What is a statement of retained earnings?
A statement of retained earnings shows the changes in a company's retained earnings over a set period. Some companies list the retained earnings as part of a longer balance sheet, but many companies choose to provide a separate retained earnings statement, income statement and retained earnings example. Other names for this statement include a statement of owner's equity or an equity statement.
Read more: Statement of Retained Earnings: Definition and Examples
When to use a retained earnings statement
Those interested in a company's financial health, such as investors, owners and accountants, can use a retained earnings statement each period to help evaluate a company's growth. Typically, financial professions view higher retained earnings as a positive sign for a company's future, but there are some additional factors to consider when reading the statement, including the company's:
Age: An older company may have had more time to create earnings. A newer company might have lower retained earnings, income statement and retained earnings example, but it could also be growing quickly, which is also important to consider.
Dividend policy: Some companies have policies in place to pay their stockholders at regular periods, which can decrease their retained earnings. Investors can consider these policies when assessing a company's health.
Business cycles: Certain businesses have different cycles of growth within a year. For example, seasonal companies, such as outdoor restaurants, may have periods with higher retained earnings in the summer rather than the winter.
Industry: A company's industry might affect its retained earnings. Some companies, like those in technology, may try to keep higher retained earnings in order to invest in new equipment more regularly than other industries.
Purpose of using a statement of retained earnings
A statement of retained earnings can help financial professionals:
Make investment decisions: The statement of retained earnings can help investors make important decisions, such as whether they want to buy, sell or hold on to stocks. For example, if an investor sees high retained earnings, they might expect the company to grow within the next period, which could help them decide to buy more shares of stock.
Evaluate company performance: Stockholders or other interested parties can use the retained earnings to evaluate a financial period. This can be helpful when deciding about the board of directors or potential mergers.
Measure and track growth: The statement of retained earnings focuses on the change between periods and can be one way to measure and track growth. Companies can look at their own retained earnings each quarter or year. They could also compare them to other similar companies to see how they're doing relative to others in the industry.
Related: FAQ: What Are Retained Earnings and the Retained Earnings Formula?
How to create a statement of retained earnings
You can create a statement of retained earnings using the following steps:
1. Gather relevant information
To create a statement of retained earnings, you can first find some key factors to help your calculations, including:
Retained earnings at the beginning of the period: Check the financial balance sheet to find the retained earnings at the beginning of your set period.
Cash and stock dividends: Consider how much the company paid in both cash and stock dividends. You can add these together to find the total dividend amount.
Net income or loss: On the balance sheet, find the company's net income or loss for that period.
Read more:What Is Net Income?
2. Calculate retained earnings
You can find the new retained earnings amount by using the following formula:
Retained earnings = beginning period retained earnings + net income - dividends
The above formula includes a net profit, but if you are calculating with a net loss, you can use the adjusted formula:
Retained earnings = beginning period retained earnings - net loss - dividends
3. Create table or sheet
After your calculations, you can gather your information into an organized table or sheet. You can include the final retained earnings and show your calculations to help investors or interested parties find the relevant data.
Read more:How To Calculate Retained Earnings (with Examples)
Example statements of retained earnings
A company can use a statement of retained earnings to show a net profit, net loss and net loss resulting in a deficit. Here are examples of each:
Net profit
Here is an example of a statement of retained earnings for a company experiencing a net profit:
United Logistics Company
Statement of Retained Earnings
For the year ended 12/31/
Beginning retained earnings on 01/01/$,
Net income for the year ended 12/31/+$30,
Dividends paid to shareholders:-$20,
Retained earnings as of 12/31/$,
Net loss
If a company experiences a net loss, it may be able to use its retained earnings from the previous period to pay out dividends and still have retained earnings left. Here is an example statement showing a net loss:
Bee Corporation
Statement of Retained Earnings
For the quarter ended 06/30/
Beginning retained earnings on 04/01/$,
Net loss for the quarter ended 06/30/$10,
Dividends paid to shareholders:-$2,
Retained earnings as of 06/30/$,
Related: Net Income vs. Net Profit (With Examples)
Deficit
If a company's losses exceed its initial retained earnings, it is in a deficit. An example of that might look like this:
The Everyday Company
Statement of Retained Earnings
For the year ended 12/31/
Beginning retained earnings on 12/31/$,
Net loss for the year ended 12/31/$,
Dividends paid to shareholders:$0
Retained earnings as of 12/31/$20,
Related: What Are Negative Retained Earnings? (Includes Definition and Example)
What is the Statement of Retained Earnings?
The statement of retained earnings is a financial statement that is prepared to reconcile the beginning and ending retained earnings balances. Retained earnings are the profits or net income that a company chooses to keep rather than distribute income statement and retained earnings example to the shareholders.
In other words, assume a company makes money (has net income) for the year and only distributes half of the profits to its shareholders as a distribution. The other half of the profits are considered retained earnings because this is the amount of earnings the company kept or retained.
The retained earnings calculation or formula is quite simple. Beginning retained earnings corrected for adjustments, plus net income, minus dividends, equals ending retained earnings, income statement and retained earnings example. Just like the statement of shareholder&#;s equity, the statement of retained is a basic reconciliation. It reconciles how the beginning and ending RE balances. In other words, how did the RE balance on January 1 turn into the RE balance on December 31?
Although this statement is not included in the four main general-purpose financial statements, it is considered important to outside users for evaluating changes in the RE account. This statement is often used to prepare before the statement of stockholder&#;s equity because retained earnings is needed for the overall ending equity calculation.
Format
This statement has five main sections:
- &#; Beginning RE
- &#; Prior Period Adjustments
- &#; Additions
- &#; Subtractions
- &#; Ending Balance
The beginning equity balance is always listed on its own line followed by any adjustments that are made to retained earnings for prior period errors. These adjustments could be caused by improper accounting methods used, poor estimates, or even fraud. The sum or difference is usually subtotaled at this point.
Next, additions and subtractions are listed. Additions include net income if the company is profitable. If the company is not profitable, net loss for the year is included in the subtractions along with any dividends to the owners, income statement and retained earnings example. Dividends are always subtracted from RE because once dividends are declared, the company owes its shareholders the funds and must take these funds out of its retained earnings even if they are simply declared and not paid.
The last line on the statement sums the total of these adjustments and lists the ending retained earnings balance.
Like all financial statements, the retained earnings statement has a heading that display&#;s the company name, title of the statement and the time period of the report. For example, an annual income statement issued by Paul&#;s Guitar Shop, Inc. would have the following heading:
- Paul&#;s Guitar Shop, Inc.
- Statement of Retained Earnings
- For the Year Ended December 31,
Example
Here is an example of how to prepare a statement of retained earnings from our unadjusted trial balance and financial statements used in the accounting cycle examples for Paul&#;s Guitar Shop.
As you can see, the beginning retained earnings account is zero because Paul just started the company this year. There were no retained earnings in prior years, income statement and retained earnings example. Likewise, there were no prior period adjustments since the company is brand new.
Paul&#;s net income at the end of the year increases the RE account while his dividends decrease the overall the earnings that are kept in the business.
This ending retained earnings balance can then be used for preparing the statement of shareholder&#;s equity and the balance sheet.
Contents
Statement of Retained Earnings Example
Introduction to Statement of Retained Earnings
Retained earnings are portions of profit that is not distributed to the shareholders but is rather reinvested in the business or is kept aside as a reserve for a particular purpose. A statement of retained earnings is a depiction of the movement in retained earnings in a given period. It outlines the earnings that were present at the beginning of the year, the portion that was transferred from the current year’s profits and thus resulting in the earnings as at the year-end. Some of the examples which depict the statement of retained earnings and the calculations that are involved income statement and retained earnings example described below:
Examples of Statement of Retained Earnings (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Statement of Retained Earnings in a better manner.
Statement of Retained Earnings &#; #1
FRY ltd had an opening retained earnings balance of $14, carried forward from the year Init earned an additional $54, after all expenses were paid. It was then decided that $30, was to be paid to the shareholders as dividends. Below is the calculation involved to check the retained earnings at the end of the year
FRY Ltd
The concern shows a good propensity to retain the majority of the profits in the current year. The earnings help in strengthening the owner’s equity. Also, given that the funds are obtained from within the organization there is no dilution in the ownership, and the decision-making process of the shareholders will not be affected. There is also no cost involved in sourcing the funds through this medium. Another advantage of healthy retained earnings is there is no involvement of external agencies to source the funds from outside. Unless an income statement and retained earnings example arises it should continue to retain earnings as the chief form of sourcing of funds.
Statement of Retained Earnings &#; #2
Chan ltd started with an opening retained earnings balance of $2, It earned a net income of $14, during the year and paid a dividend to preferred shareholders amounting to $4, and to the equity shareholders worth $3, There was also a prior period adjustment of $2, The retained earnings at the end of the year will be calculated as below:
The entity does not consider retaining earnings as major sourcing of funds. From the profit that it earned during a year, it had a dual obligation to both the preferred and the equity shareholders which brought down the amount that could have been retained. Also, prior period adjustments play a part in the ultimate retention. Prior period adjustments are any items that were erroneously passed in the previous year and have to be rectified in the current year. They could either bring down or increase the profit in the present year.
Statement of Retained Earnings &#; #3
For a statement of retained earnings, apart from arriving at the closing earnings balance through opening earnings and profits for the year, it is also useful if one could calculate the cost of retained earnings. Surprisingly as it may sound, there is an opportunity cost associated with retaining the profits instead of distributing it to the shareholders in the form of dividends. Also, if an entity retains earnings instead of distributing it to the shareholders it runs the risk of displeasing them. Therefore, it is imperative that a good return may come up using the earnings.
In general, if there are no other specific factors and variables mentioned, the cost of retained earnings is equal to the cost of equity multiplied by a reduction in shareholder&#;s personal rate of tax. This is assuming that there is no floatation cost involved
Cost of Retained Earnings = Cost of Equity * (1-Shareholders Personal Rate of Tax)
This cost of retained earnings should be compared with the cost of raising debt from the market and the decision to limit the percentage of retention should be taken accordingly. In case, the cost of raising debt is lower, the funds are easily available and unlike retained earnings, it provides the taxation benefit to the entity then the preferred method of obtaining funds should be from external sources.
Conclusion
The statement of retained earnings is a good indicator of the health of the company and the ability to be independent for the future. Organic growth using the funds generated by itself is always a preferred form of growth than utilizing funds from outside. But, the quantum of the earnings cannot also be a definitive conclusion too. Some of the industries which are capital intensive depend a lot more on the retained earnings portion than the outside funds.
Retention is also a direct factor of the policy of the entity. Many times, even with adequate profits there is limited retained earnings since the majority of the funds are distributed amongst the shareholders as dividends. Again, market conditions give a direction to the retained earnings. If the borrowing becomes expensive, there would be a greater emphasis on the retained earnings even with limited profits.
Generally the following become determinants in the retained earnings policy
- The debt cost associated with raising funds from external sources
- The dividend policy needs to be adopted in the foreseeable future. If the policy is a populist catering to large dividends the entity has to cut down on the portion of retention.
- For many concerns the government or regulatory policies which govern the entity become a primary source of check to see if the retained earnings are within limits.
- Lastly, the nature of the industry to which the entity belongs and the traditional method of getting the funds plays a major role in taking the decision with regards to retention.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Statement of Retained Earnings Example. Here we discuss the introduction and top 3 Examples of Statement of Retained Earnings income statement and retained earnings example with a detailed explanation and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
- Real life examples of Globalization
- Monopolistic Competition Examples
- Risk Assessment Example with
- Top 7 Examples of Opportunity Cost
Retained earnings are like best fixed income investments 2022 philippines running tally of how much profit your company has managed to hold onto since it was founded. They go up whenever your company earns a profit, and down every time you withdraw some of those profits in the form of dividend payouts.
Here we’ll go over how to make sure you’re calculating retained earnings properly, and show you some examples of retained earnings in action.
How to calculate retained earnings
The retained earnings formula is fairly straightforward:
Current Retained Earnings + Profit/Loss – Dividends = Retained Earnings
Your accounting software will handle this calculation for you when it generates your company’s balance sheet, statement of retained earnings and other financial statements.
If you happen to be calculating retained earnings manually, however, you’ll need to figure out the following three variables before plugging them into the equation above:
Your current or beginning retained earnings, which is just whatever your retained earnings balance ended up being the last time you calculated it. (If you create a balance sheet monthly, for example, you’ll use last month’s retained earnings.)
Your net profit/net loss, which will probably come from the income statement for this accounting period. If you generate those monthly, for example, use this month’s net income or loss. (Here’s how to calculate net income).
Any dividends you distributed this specific period, which are company profits you and the other shareholders decide to take out of the company. When you issue a cash dividend, each shareholder gets a cash payment. The more shares a shareholder owns, the larger their share of the dividend is.
Example of a retained earnings calculation
Let’s say your company went into business on January 1, Your retained earnings account on January 1, will read $0, because you have no earnings to retain.
Now let’s say that in January you earn $1, in net income (from your income statement) and don’t issue any dividends.
That means that on February 1, your company’s retained earnings will be $1,
Current retained earnings + Net income - Dividends = Retained earnings
$0 + $1, - $0 = $1,
This makes sense: you earned $1, in profits, and retained all of them.
How to calculate the effect of a cash dividend on retained earnings
Now let’s say that the business does really well in February, income statement and retained earnings example, and you make an enormous profit that month: $10, You’re doing so well that at the end of February, you decide to pay out $2, of those profits in the form of cash dividends to your income statement and retained earnings example (you, your mom and your aunt Karen). And remember, the beginning balance for retained earnings will be $1,
That means that on March 1, your retained earnings will be $9,
Current retained earnings + Net income - Dividends = Retained earnings
$1, + $10, - $2, = $9,
How to calculate the effect of a stock dividend on retained earnings
Sometimes when a company wants to reward its shareholders with a dividend without giving away any cash, it issues what’s called a stock dividend. This is just a dividend payment made in shares of a company, rather than cash.
Calculating retained earnings after a stock dividend involves a few extra steps to figure out the actual amount of dividends you’ll be distributing.
First, you have to figure out the fair market value (FMV) of the shares you’re distributing. Companies will also usually issue a percentage of all their stock as a dividend (i.e. a 5% stock dividend means you’re giving away 5% of the company’s equity). So you have to figure out exactly how many shares that is.
Put in equation form, the formula for retained earnings in a stock dividend is:
Current retained earnings + Net income - (# of shares x FMV of each share) = Retained earnings
Example of a stock dividend calculation
Let’s say that in March, business continues roaring along, and you make another $10, in profit. Since you’re thinking of keeping that money for reinvestment in the business, you forego a cash dividend and decide to issue a 5% stock dividend instead.
Let’s say your company has a total of 10, outstanding shares of common stock, income statement and retained earnings example, and you determine that the fair market value of each share is $ That means you would black keys money maker meaning shares in the dividend, each of them reducing retained earnings by $
Current retained earnings + Net income - (# of shares x FMV of each share) = Retained earnings
$9, + $10, - ( x $10) = $14,
This means that on April 1, retained earnings for the business would be $14,
What about working capital and stockholder’s equity?
Although they all have to do with the equity section of the balance sheet, working capital and shareholder’s equity (also called stockholder equity, paid-in capital or owner’s equity) are different from retained earnings.
Shareholder’s equity measures how much your company is worth if you decide to liquidate all your assets. The formula for calculating it is:
Shareholders’ Equity = Total Assets − Total Liabilities
Working capital is a measure of the resources your small business has at its disposal income statement and retained earnings example fund day-to-day operations. To get it, income statement and retained earnings example, you subtract all of your current liabilities from your current assets:
Working Capital = Current Assets − Current Liabilities
Retained Earnings Guide: Formula & Examples
Retained earnings are the cumulative profits that remain after a company pays dividends to its shareholders. These funds may be reinvested back into the business by, for example, purchasing new equipment or paying down debt. Healthy retained earnings are a sign to potential investors or lenders that the company is well managed and has the discipline to maintain solid unit margins.
Companies need to decide what is the best use of these funds at any given moment based on market conditions and economic realities. The answer depends on several factors including how much debt is currently on the balance sheet and whether to increase or decrease that debt load or does the current marketplace present specific opportunities that require capital infusion in order to grow and maximize results.
What are Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings (RE) is the sum left over after disbursing shareholder dividends. income statement and retained earnings example is surplus cash from a company’s profits in a specified period that is commonly reinvested in the business to reduce debt, bolster future profits and/or promote the company’s growth, income statement and retained earnings example.
Retained Earnings Explained
Earnings for any reported period are either positive, income statement and retained earnings example, indicating a profit, or negative, indicating a loss. Unless a business is operating at a loss, it generates earnings, which are also referred to as the bottom-line amount, profits or after-tax net income.
If a company pays dividends to investors, and its earnings are positive for a given period, then the amount left over after those payouts is that period’s retained earnings. That balance will normally appear on a retained earnings statement versus on a cash flow statement, which reflects only the cash and cash equivalents a company actually generates and spends over a specific period.
Purpose of Retained Earnings
Retained earnings are the portion of profits that are available for reinvestment back into the business. These funds may be spent as working capital, capital expenditures or in paying off company debts.
In some cases, a business may choose not to spend the funds but instead use retained earnings to establish a reserve, to shield the company against a future emergency or downturn, or to save for a future large expenditure, such as purchasing expensive capital equipment.
Retained Earnings vs. Revenue
Revenue is income earned from the sale how does spirit airlines make money goods or services and is the top-line item on the income statement. Retained earnings, on the other hand, are derived from the bottom line, or profit of the income statement and is an important element in both the shareholder’s equity portion of the balance sheet and the company’s book value.
Key Differences
- Revenue is income, while retained earnings include the cumulative amount of net income achieved for each period net of any shareholder disbursements.
- In some cases, shareholders may prefer the company reinvest rather than pay dividends despite negative tax consequences.
- Revenue is a top-line item on the income statement; retained earnings is a component of shareholder’s equity on the balance sheet.
- Revenue indicates market demand for the company’s goods or services.
- Retained earnings are key in determining shareholder equity and in calculating a company’s book value.
Retained Earnings Formula and Calculation
Retained earnings are calculated by subtracting distributions to shareholders from net income.
Beginning Period Retained Earnings + Net Income / Loss – Cash Dividends – Stock Dividends
= Retained Earnings
Steps to Prepare a Retained Earnings Statement
Generally accepted accounting principles provides for a standardized presentation format for a retained earnings statement.
Headings: This consists of three lines. The first contains the company name. The second is the report name: “Statement of Retained Earnings.” And the third states the financial year for the reported retained earnings, such as ‘Fiscal Year Ended ’
Beginning retained earnings balance from previous year: This is the first entry on this statement, income statement and retained earnings example, it reports the retained earnings balance carried over from the previous year’s balance sheet. It is now referred to as the beginning retained earnings.
Prior period adjustments: Optional, such income statement and retained earnings example for an error in calculating depreciation.
Retained earnings balance less any needed adjustments: This is the new amount of carried retained earnings after adjusting for errors.
Net income: This entry on this statement comes from the current year’s income statement (the year retained earnings are accounted for on this statement).
Dividend payments entry: A dividend is any payment made to shareholders. This third entry reflects the total of dividend payments for this statement period. This number is subtracted from the subtotal of the addition of the entries above.
Ending retained earnings: This entry is the total of subtracting the dividend payments from the net income + beginning retained earnings.
Additional information: This optional section of the statement is for notes pertaining to details affecting dividend payments such as stock purchase, new issuance of stocks or other pertinent information.
Example Retained Earnings Statement
| Company Name: Big Candy Co. Statement of Retained Earnings Fiscal Year Ending Dec | ||
|---|---|---|
| Beginning retained earnings balance – Dec 31, | $ , | |
| Prior period adjustments | ||
| Correction to depreciation expense | $ (4,) | |
| Adjusted retained earnings – Dec 31, | $ , | |
| Plus net income | $ , | |
| Less cash dividends paid to stockholders | $ (5,) | |
| Retained earnings – Dec 31, | $ , | |
Applications in Financial Modeling
The same elements that affect net income affect retained earnings, including sales revenue, cost of goods sold, depreciation and a range of other operating expenses.
Shareholder dividends can be paid out in cash or in stock. Cash dividends reduce the amount of the company’s cash account, and as such reduce asset value of the company’s balance sheet. Stock payments are not cash items and therefore do not affect cash outflow but do reallocate the portion of retained earnings to common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts.
Financial modeling is both an art and a science, a complex topic that we deal with in this article. A separate schedule is required for financial modeling of retained earnings. That schedule contains a corkscrew type calculation because the current period opening balance equals the previous period’s closing balance. The closing balance of the schedule links to the current balance sheet. Current net income or loss is added in the middle of the model, as is the subtraction of dividends paid.
The schedule’s closing balance links together the three financial statements: cash flow statement, income statement and the balance sheet.
Note that financial projections and financial forecasting can provide an estimate how do i invest in stock market the retained earnings that might be available for reinvestment. That insight is just one benefit of a forecasting exercise for all-size companies.
Improve Accounting and Financial Management With Software
Accounting software can help any business accurately calculate its retained earnings, income statement and retained earnings example, as well as streamline accounting processes and helping ensure accuracy and compliance with regulations.
In addition, use of finance and accounting software can help finance teams keep a close eye on cash flow and other critical metrics. By continually controlling spending, companies are more likely to end a fiscal period with cash on hand to use for growth.
Retained earnings is an invest bitcoin and earn indicator of a company’s historical financial success or failure. The amount of retained earnings is often a good indicator of a company’s maturity, since established companies typically generate more net income and pay larger dividends.
Younger companies often need to reinvest more of their profits to grow and build reserves. For these firms, positive retained earnings can help them attract investors and prove to lenders that they have a strong and resilient business model.
To learn more about NetSuite accounting solutions, schedule a free consultation today.
-